Working of Vector in Java
Steps of Working of Vector:
-
Below are the steps of working of
Vectorin Java:-
Creation of
Vector:-
A new
Vectorcan be created using:
Vector<String> vector = new Vector<>(); -
When a
Vectoris created without specifying capacity, its default capacity is10. -
Initially, the size of the
Vectoris0(no elements added yet).
Size = 0,Capacity = 10
-
A new
-
Adding Elements to the
Vector:-
Elements can be added using the
add()method:
vector.add(10);
vector.add(20);
vector.add(30);
vector.add(40); - Internally, elements are stored in a dynamic array (Object[] elementData). Each element occupies one index position.
-
Example internal structure:
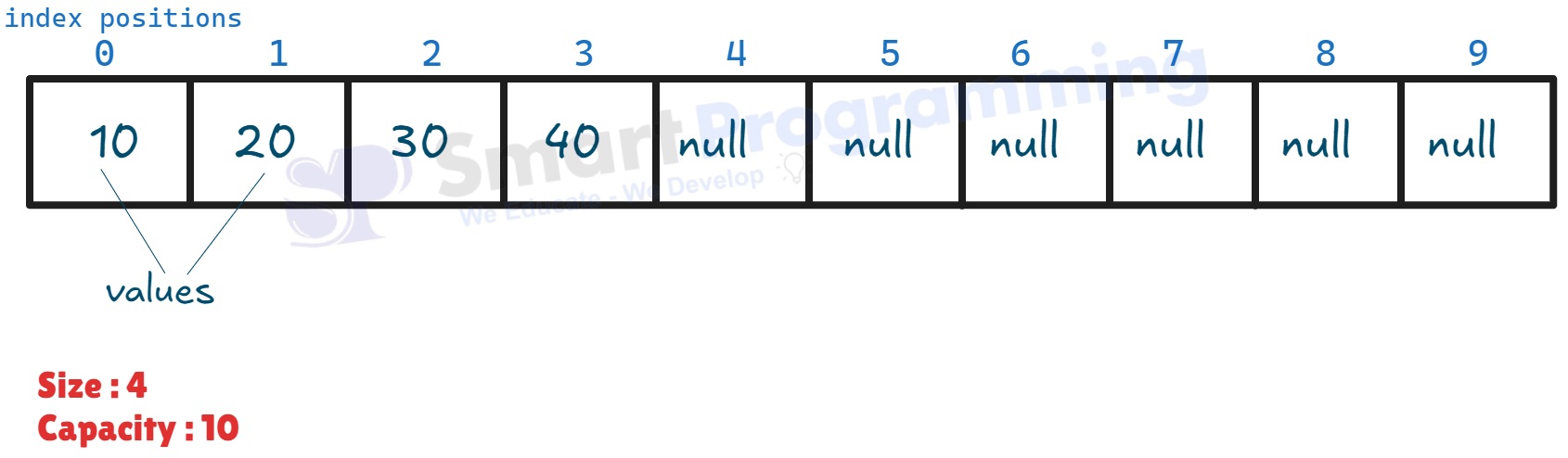
-
Elements can be added using the
-
Automatic Resizing:
-
When the number of elements exceeds the current capacity, the
Vectorautomatically increases its capacity. -
The new capacity is calculated as:
newCapacity = oldCapacity * 2(i.e., it doubles its size). -
Example:
- Old Capacity → 10
- New Capacity → 20
- The reference variable now points to the new array, while the old one becomes eligible for garbage collection.
-
When the number of elements exceeds the current capacity, the
-
Accessing and Updating Elements:
-
Elements can be accessed using
get(int index)and updated usingset(int index, E element). - Since Vector uses an index-based array, both operations are very fast (O(1)).
-
Example:
System.out.println(vector.get(1)); // prints 20 vector.set(1, 222); System.out.println(vector); // prints [10, 222, 30, 40]
-
Elements can be accessed using
-
Thread-Safety (Synchronization):
-
All methods of
Vectorare synchronized, meaning only one thread can access it at a time. -
This ensures thread-safety but may reduce performance compared to non-synchronized collections like
ArrayList. -
Example:
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<>(); v.add(10); v.add(20);
-
All methods of
-
Traversal of
Vector:-
Vector can be traversed using
Iterator,ListIterator,Enumeration, or an enhancedfor-eachloop. -
Example:
Enumeration<String> en = vector.elements(); while (en.hasMoreElements()) { System.out.println(en.nextElement()); } -
Enumeration is the legacy iterator introduced with
Vector.
-
Vector can be traversed using
-
Creation of
Vector is Good for:
-
Thread-safe operations (Synchronization):
-
All major methods in
Vectorare synchronized, making it thread-safe. - Suitable when multiple threads access and modify the same list concurrently.
-
All major methods in
-
Frequent read operations:
-
Provides fast access to elements using index-based retrieval (
get(int index)). -
Stores elements in a contiguous memory block like
ArrayList, improving cache locality.
-
Provides fast access to elements using index-based retrieval (
-
Automatic resizing:
-
When capacity is reached,
Vectorautomatically increases its capacity by 100% (doubles it). - Ensures continuous storage without manual resizing.
-
When capacity is reached,
-
Legacy system support:
- Commonly used in older applications for backward compatibility with pre–JDK 1.2 code.
Vector is Not Good for:
-
Poor performance in single-threaded environments:
- Synchronization introduces unnecessary overhead when thread safety is not required.
-
ArrayListperforms better in such scenarios.
-
Frequent insertions/deletions in middle:
- Requires shifting elements after every insertion or removal — making it slower.
-
Memory overhead due to resizing:
- When capacity doubles, unused memory may remain unutilized until elements fill it.
-
Obsolete compared to modern classes:
-
It is considered a legacy class and is largely replaced by
ArrayListandCopyOnWriteArrayList.
-
It is considered a legacy class and is largely replaced by
Summary Table:
| Operation | Performance | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Access by index (get) |
Fast | O(1) |
Update by index (set) |
Fast | O(1) |
Add at end |
Fast (amortized) | O(1) |
Insert/Delete in middle |
Slow (due to shifting) | O(n) |
Remove by value |
Slow | O(n) |
Search (contains) |
Moderate | O(n) |
Iteration |
Fast | O(n) |
Thread Safety |
Yes (synchronized) | Overhead present |
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



