Vector Legacy Class in Java
Introduction
-
Vector is a legacy class in Java that implements the List interface.
- It is known as a legacy class because it was introduced in JDK 1.0 and later modified and integrated into the Java Collections Framework.
- It is primarily retained for legacy code compatibility and is therefore used very infrequently in modern Java applications.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.0 as part of the original Collection classes.
-
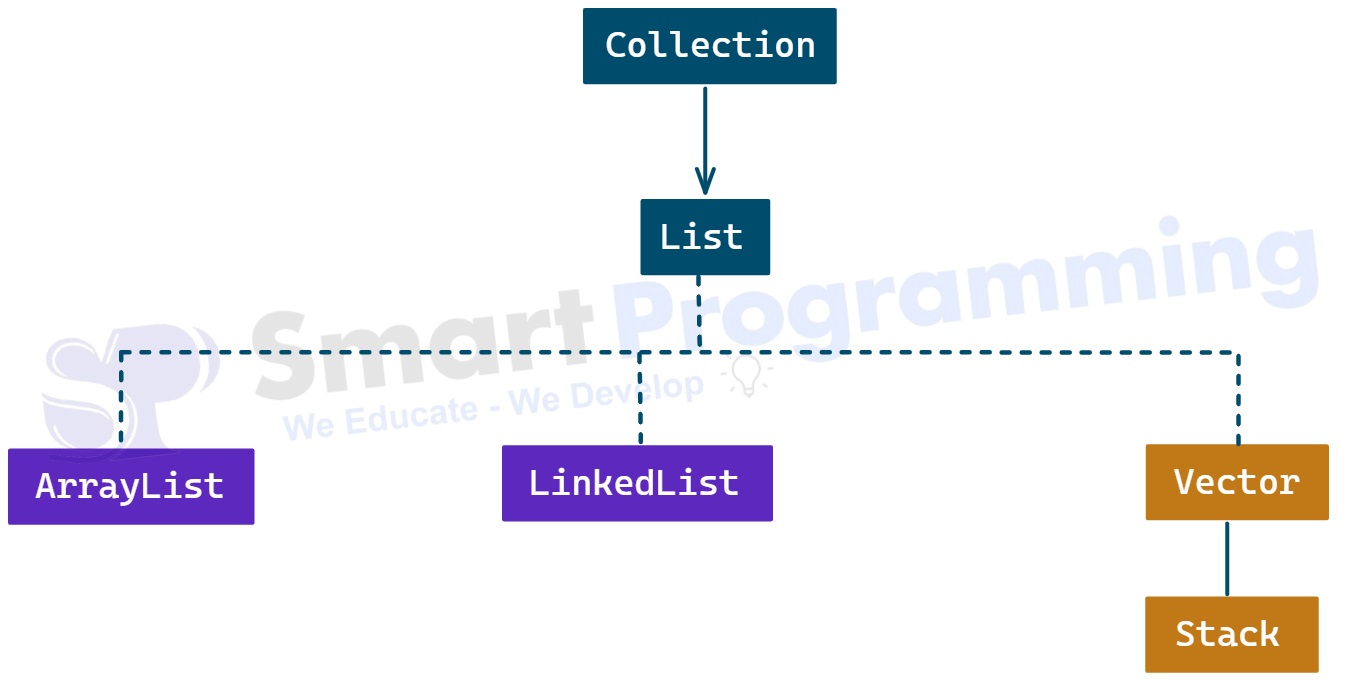
Hierarchy:
-
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public class Vector<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // Constructors // Methods // Fields }-
Vectorimplements theListinterface, making it part of the Java Collection Framework (after JDK 1.2). -
It implements
RandomAccess, so elements can be accessed quickly by index (likeArrayList).
-
-
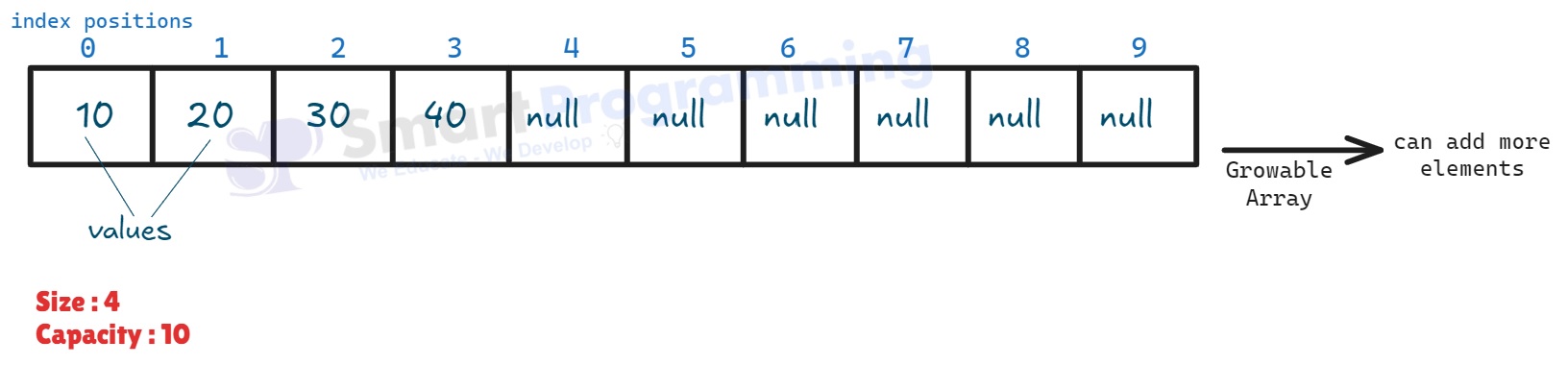
Vectoris a growable array that stores elements dynamically, similar toArrayList.
Constructors of Vector Class
-
Below are the constructors defined in the
Vectorclass:
| Sr. No. | Constructor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vector() |
Constructs an empty Vector with an initial capacity of 10. |
| 2 | Vector(int initialCapacity) |
Constructs an empty Vector with the specified initial capacity. |
| 3 | Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) |
Constructs an empty Vector with the specified initial capacity and capacity increment. |
| 4 | Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) |
Constructs a Vector containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order returned by the collection’s iterator. |
Methods of Vector Class
-
Below are some methods defined specifically in the
Vectorclass:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | void addElement(E obj) |
Adds the specified element to the end of the Vector. |
| 2 | void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) |
Inserts the specified element at the specified position in the Vector. |
| 3 | E elementAt(int index) |
Returns the element at the specified index in the Vector. |
| 4 | E firstElement() |
Returns the first element in the Vector. |
| 5 | E lastElement() |
Returns the last element in the Vector. |
| 6 | void removeElementAt(int index) |
Removes the element at the specified position in the Vector. |
| 7 | boolean contains(Object obj) |
Tests whether the Vector contains the specified element. |
| 8 | void removeAllElements() |
Removes all elements from the Vector. |
| 9 | void setElementAt(E obj, int index) |
Replaces the element at the specified position with the specified element. |
| 10 | void removeElement(Object obj) |
Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from the Vector. |
Note :
-
Vectorinherits all the methods ofList,RandomAccess, andCollectioninterfaces. - It is a synchronized class and can be used as a list or stack.
Program :
-
In below program, we are directly using the
Vectorclass. -
import java.util.Vector; public class VectorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector<String> vector = new Vector<>(); // Adding elements vector.add("Apple"); vector.add("Banana"); vector.add("Mango"); vector.add("Banana"); // duplicate allowed System.out.println(vector); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Accessing first and last elements System.out.println("First Element: " + vector.firstElement()); System.out.println("Last Element: " + vector.lastElement()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Updating element vector.set(1, "Orange"); System.out.println(vector); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Removing element vector.remove("Apple"); System.out.println(vector); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Using Vector as a Stack vector.add(0, "Grapes"); // equivalent to push at beginning vector.add("Pineapple"); // add at end System.out.println(vector); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating Vector for(String fruit : vector) { System.out.println(fruit); } } }Output:
[Apple, Banana, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- First Element: Apple Last Element: Banana ------------------------- [Apple, Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- [Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- [Grapes, Orange, Mango, Banana, Pineapple] ------------------------- Grapes Orange Mango Banana Pineapple
⚠️ Note:
Vectoris a legacy class in Java and is rarely used nowadays.- It is fully synchronized and slower than modern alternatives like
ArrayList.
Properties of Vector Class:
- Vector is an index-based data structure, which means the first element is inserted at
index 0. - Vector can store different data types or heterogeneous elements if generics are not used.
- We can store duplicate elements in the Vector.
- We can store null values in the Vector.
- Vector follows the insertion order, meaning elements are retrieved in the same sequence they were added.
- Vector does not follow the sorting order; sorting must be done explicitly using
Collections.sort()orlist.sort(). - Vector is synchronized, making it thread-safe for individual operations.
- Vector guarantees for data consistency.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.