Working of LinkedList in Java
Steps of Working of LinkedList:
-
Below are the steps of working of
LinkedListin Java:-
Creation of
LinkedList:-
A new
LinkedListcan be created using:
LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); -
Initially, the
LinkedListis empty — it has no nodes. The head and tail both point tonull. -
Internal structure at the beginning:
Head → null,Tail → null,Size = 0
-
A new
-
Adding the First Element:
-
When we add the first element using
add():
list.add("A"); -
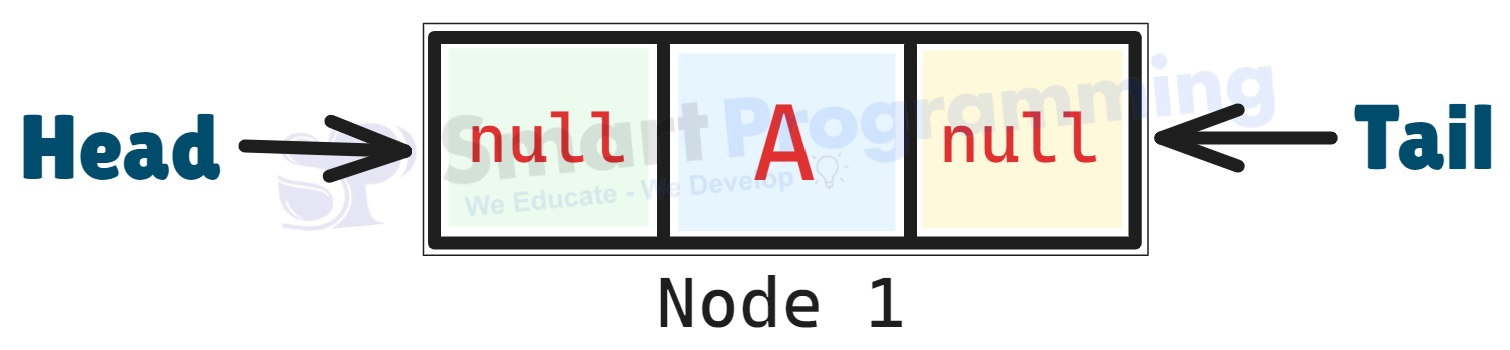
A new Node is created that contains:
- Data → "A"
- Previous →
null - Next →
null - Size →
0
-
Both head and tail point to this single node.
-
When we add the first element using
-
Adding More Elements:
-
When we add more elements, new nodes are created and connected sequentially.
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add("D"); -
Each new node is linked at the end of the list:
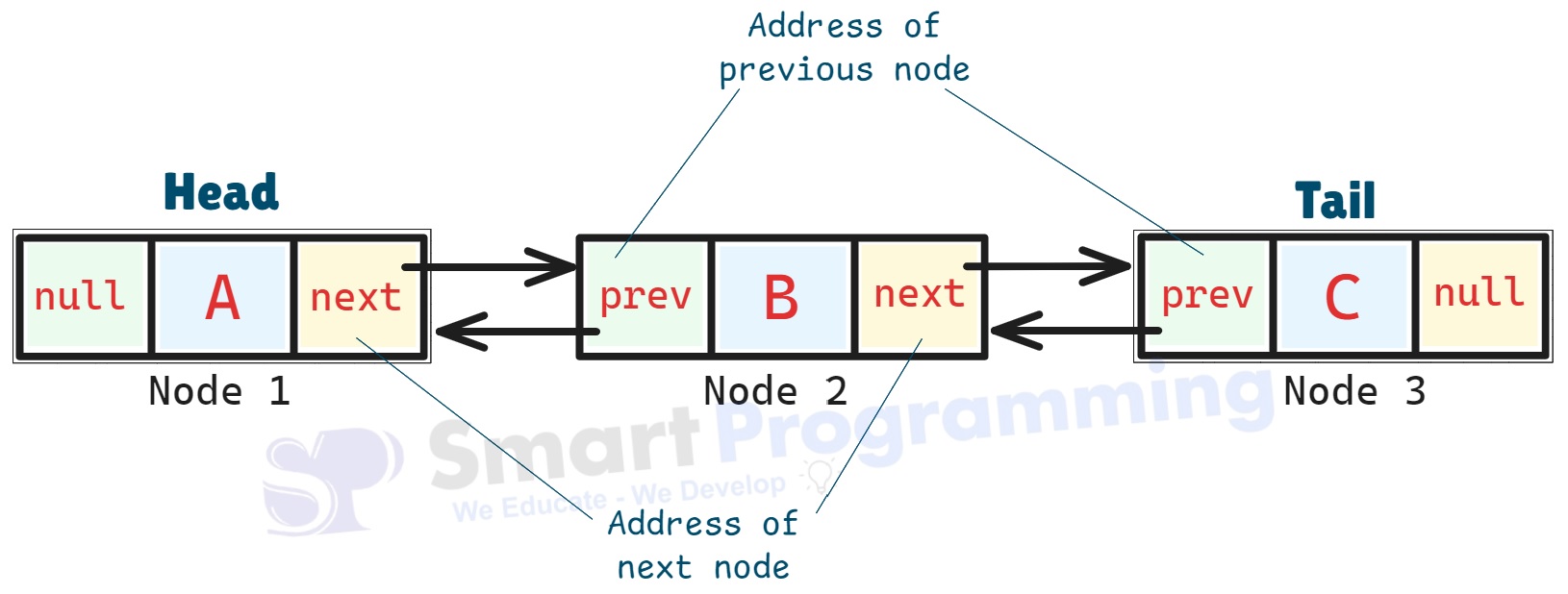
- The Previous pointer of each node points to the previous element, and the Next pointer points to the next element — making it a Doubly Linked List.
-
When we add more elements, new nodes are created and connected sequentially.
-
Adding or Deleting Elements in the Middle:
- When inserting or deleting (removing) elements in the middle, the surrounding nodes’ pointers are adjusted.
-
Example – inserting
"X"between"B"and"C":
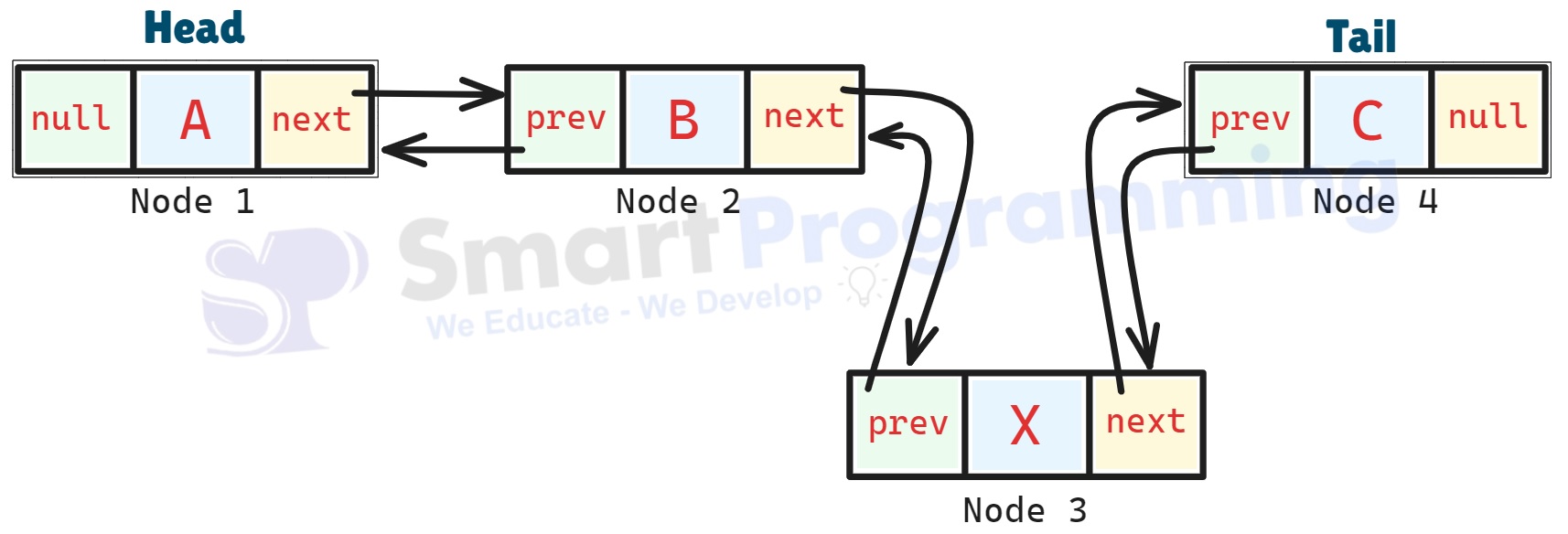
- The Previous and Next references of neighboring nodes are updated accordingly.
-
Traversal of
LinkedList:-
The
LinkedListis traversed sequentially from head to tail usingIteratororListIterator. -
Example:
Iterator<String> itr = list.iterator(); while (itr.hasNext()) { System.out.println(itr.next()); } -
Unlike
ArrayList, elements are not accessed using indexes directly; instead, traversal follows node links.
-
The
-
Creation of
LinkedList is Good for:
-
Insertion and Deletion at the beginning, middle or end:
- Each element (called a node) contains a reference to the previous and next node.
-
Insertion and deletion only involve changing the links, not shifting elements like in
ArrayList.
-
Frequent modifications (add/remove):
- Performs efficiently when elements are frequently added or removed from different positions.
-
Memory management of variable-size data:
- Each node is allocated separately in memory, allowing dynamic growth without resizing.
LinkedList is Not Good for:
-
Accessing elements by index (
get(int index)):- Slow because traversal starts from the head or tail node to reach the given index (no direct access).
-
Memory overhead:
-
Each node stores extra references (
nextandprev), consuming more memory.
-
Each node stores extra references (
-
Poor cache locality:
-
Nodes are scattered in memory (non-contiguous), resulting in slower iteration compared to
ArrayList.
-
Nodes are scattered in memory (non-contiguous), resulting in slower iteration compared to
-
Random access operations:
- Since nodes are connected by references, random access takes O(n) time.
Summary Table:
| Operation | Performance | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Access by index (get) |
Slow | O(n) |
Update by index (set) |
Slow | O(n) |
Add at beginning/end |
Fast | O(1) |
Insert in middle |
Fast (if reference known) | O(1) for known node, otherwise O(n) |
Remove by node |
Fast (if reference known) | O(1) for known node, otherwise O(n) |
Search (contains) |
Slow | O(n) |
Iteration |
Slower | O(n), not cache-friendly |
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



