Stack Legacy Class in Java
Introduction
-
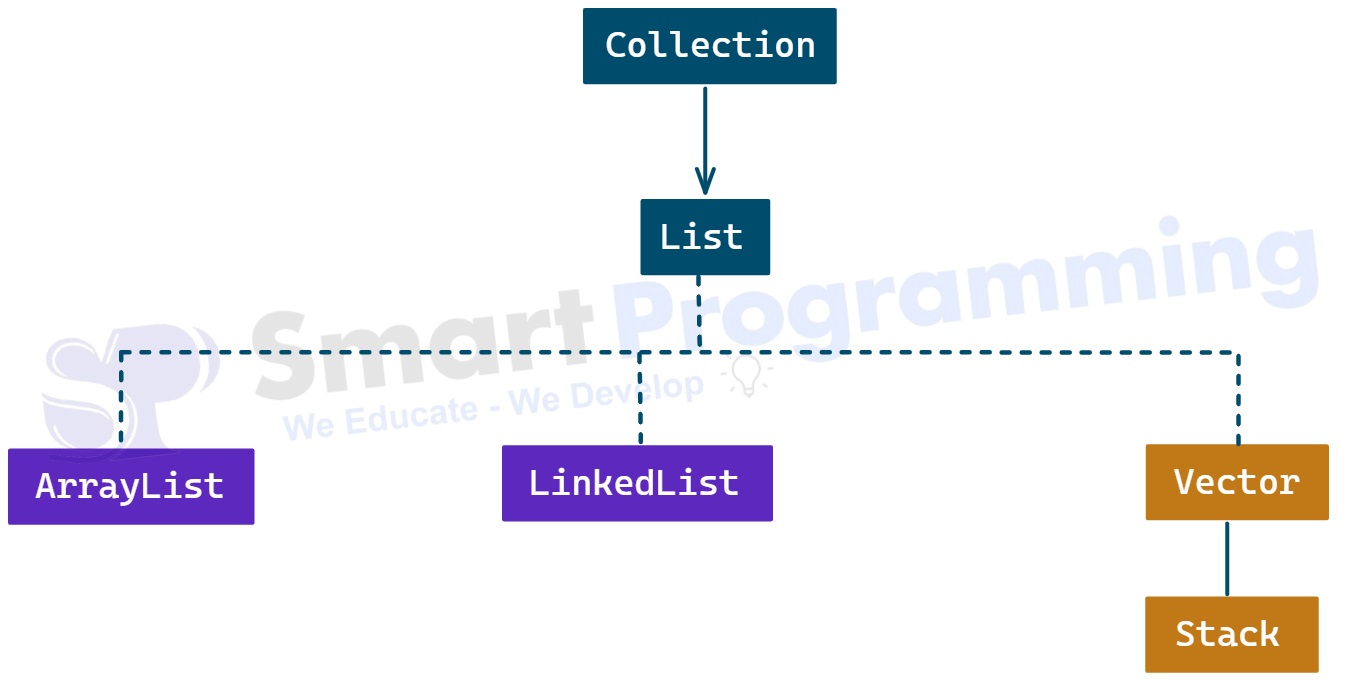
Stack is a legacy class in Java that extends the Vector class.
- It is known as a legacy class because it was introduced in JDK 1.0 and later modified and integrated into the Java Collections Framework.
- It is primarily retained for legacy code compatibility and is therefore used very infrequently in modern Java applications.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.0 as part of the original Collection classes.
-
Hierarchy:
-
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> { // Constructors // Methods // Fields }-
StackextendsVectorclass and inherits all its methods.
-
-
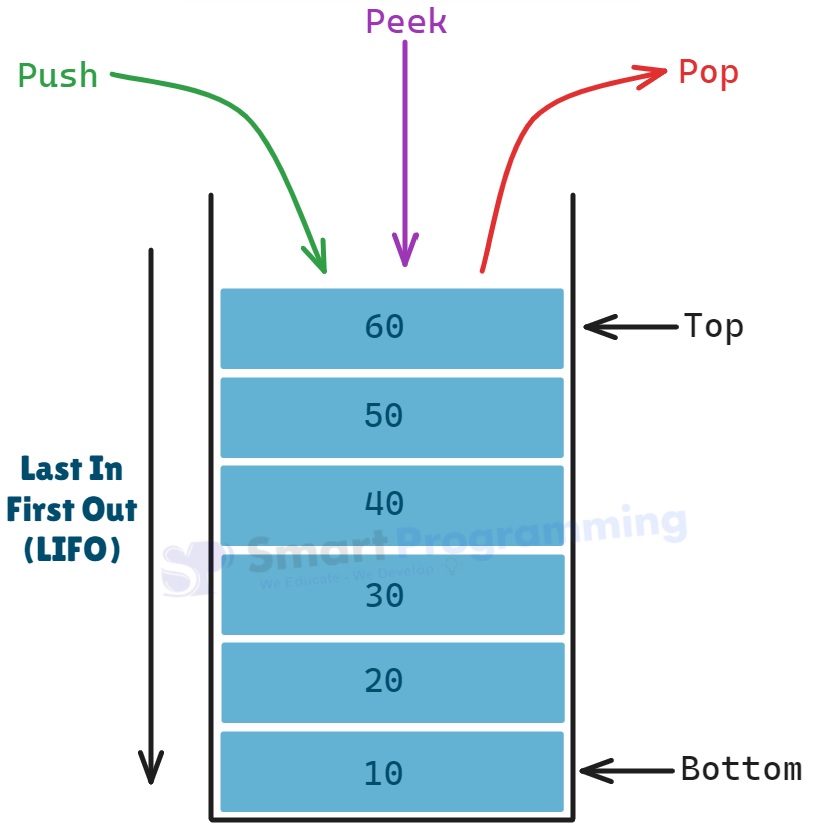
Stackis a LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) data structure where the last inserted element is the first to be removed.
Constructors of Stack Class
-
Below are the constructors defined in the
Stackclass:
| Sr. No. | Constructor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stack() |
Constructs an empty Stack with an initial capacity of 10 (inherited from Vector). |
Methods of Stack Class
-
Below are the methods defined specifically in the
Stackclass:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | E push(E item) |
Pushes (inserts) an element onto the top of the Stack and returns the element pushed. |
| 2 | E pop() |
Removes and returns the element at the top of the Stack. Throws EmptyStackException if the stack is empty. |
| 3 | E peek() |
Returns the element at the top of the Stack without removing it. |
| 4 | boolean empty() |
Tests whether the Stack is empty and returns true if no elements are present. |
| 5 | int search(Object o) |
Searches for the specified element in the Stack and returns its 1-based position from the top. Returns -1 if not found. |
Note :
-
Stackextends theVectorclass and inherits all its methods and properties. - It represents a LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) data structure commonly used in algorithms such as expression evaluation and backtracking.
-
Although
Stackis synchronized, it is not recommended for modern applications — useDeque(likeArrayDeque) instead.
Program :
-
In the below program, we are directly using the
Stackclass from thejava.utilpackage. -
import java.util.Stack; public class StackDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>(); // Pushing elements stack.push("Apple"); stack.push("Banana"); stack.push("Mango"); stack.push("Banana"); // duplicate allowed System.out.println(stack); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Accessing top element System.out.println("Top Element (peek): " + stack.peek()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Popping element System.out.println("Popped Element: " + stack.pop()); System.out.println(stack); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Searching element System.out.println("Position of 'Apple': " + stack.search("Apple")); // top is position 1 System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Checking if stack is empty System.out.println("Is Stack Empty? " + stack.isEmpty()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating Stack for(String fruit : stack) { System.out.println(fruit); } } }Output:
[Apple, Banana, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- Top Element (peek): Banana ------------------------- Popped Element: Banana [Apple, Banana, Mango] ------------------------- Position of 'Apple': 3 ------------------------- Is Stack Empty? false ------------------------- Apple Banana Mango
⚠️ Note:
Stackis a legacy class in Java that extendsVectorand is rarely used nowadays.- Modern alternatives like
DequeorArrayDequeare preferred for stack implementations.
Properties of Stack Class:
- Stack is an index-based data structure, meaning the first element is inserted at
index 0. - Stack can store heterogeneous elements if generics are not used.
- Stack allows duplicate elements.
- Stack allows null values.
- Stack maintains insertion order, but elements are accessed in LIFO (Last In First Out) manner.
- Stack does not follow sorting order; sorting must be done explicitly if needed.
- Stack extends the
Vectorclass, so it is synchronized and thread-safe. - Stack guarantees for data consistency.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.