LinkedList Class in Java
Introduction
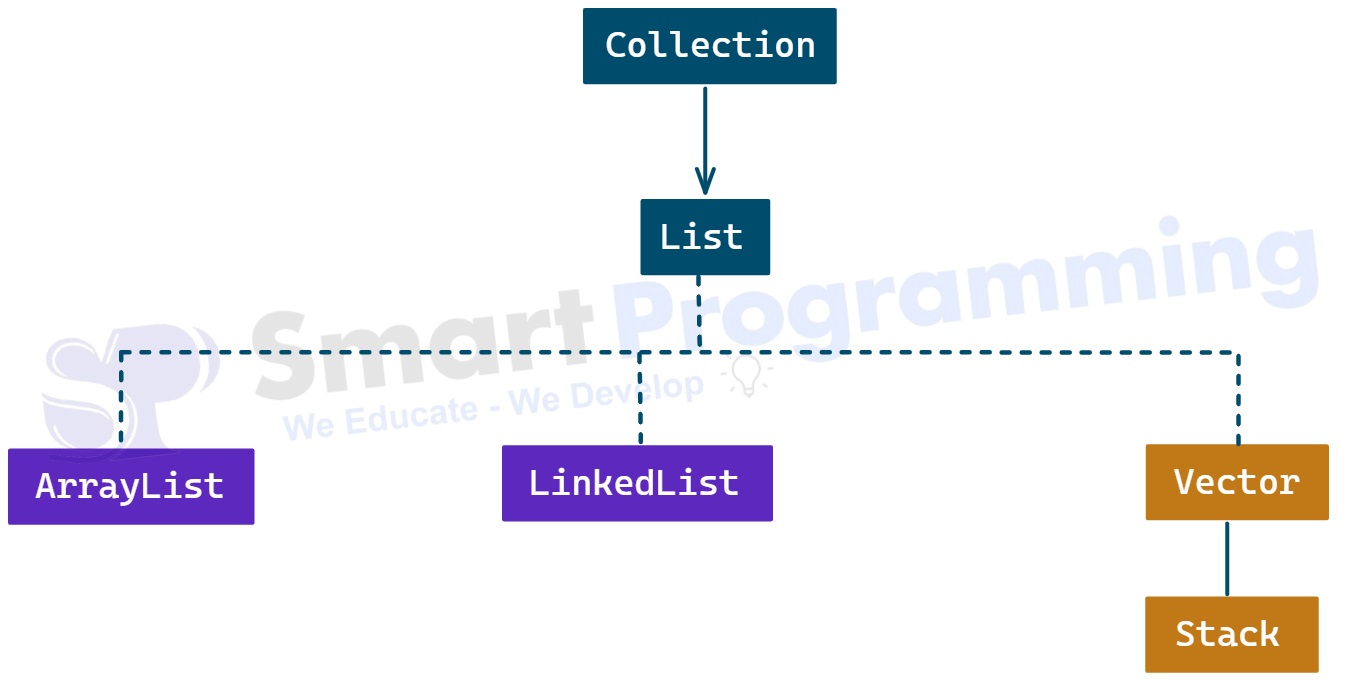
- LinkedList is an implemented class of the List and Deque interfaces.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.2 version.
-
Hierarchy:
-
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public class LinkedList<E> implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // Constructors // Methods // Fields }LinkedListimplements bothListandDequeinterfaces, so it can be used as a list, queue, or stack.- It does not implement
RandomAccess, so accessing elements by index is slower compared toArrayList.
-
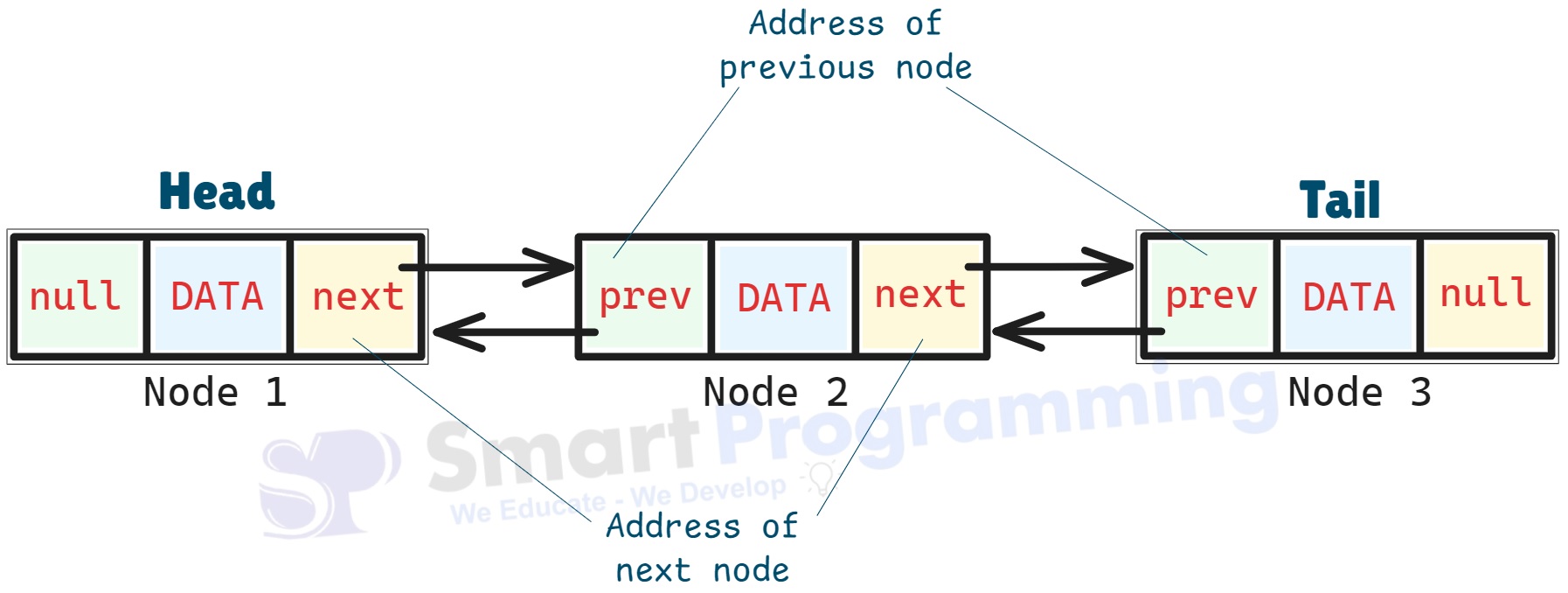
LinkedList is a doubly-linked list data structure that allows efficient insertion and deletion of elements.
Constructors of LinkedList Class
-
Below are the constructors defined in the
LinkedListclass:
| Sr. No. | Constructor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | LinkedList() |
Constructs an empty LinkedList. |
| 2 | LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) |
Constructs a LinkedList containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order returned by the collection’s iterator. |
Methods of LinkedList Class
-
Below are some methods defined specifically in the
LinkedListclass:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | void addFirst(E e) |
Inserts the specified element at the beginning of the LinkedList. |
| 2 | void addLast(E e) |
Appends the specified element to the end of the LinkedList. |
| 3 | E getFirst() |
Returns the first element in the LinkedList. |
| 4 | E getLast() |
Returns the last element in the LinkedList. |
| 5 | E removeFirst() |
Removes and returns the first element from the LinkedList. |
| 6 | E removeLast() |
Removes and returns the last element from the LinkedList. |
| 7 | void push(E e) |
Pushes an element onto the stack represented by this LinkedList. |
| 8 | E pop() |
Pops an element from the stack represented by this LinkedList. |
| 9 | boolean offer(E e) |
Inserts the specified element at the end of the queue. |
| 10 | E poll() |
Retrieves and removes the head (first element) of the queue, or returns null if the queue is empty. |
Note :
-
LinkedListinherits all the methods ofList,Deque, andCollectioninterfaces. - It can be used as a list, queue, or stack.
Program :
-
In below program, we are directly using
LinkedListclass. -
import java.util.LinkedList; public class LinkedListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { LinkedList<String> list = new LinkedList<>(); // Adding elements list.add("Apple"); list.add("Banana"); list.add("Mango"); list.add("Banana"); // duplicate allowed System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Accessing first and last elements System.out.println("First Element: " + list.getFirst()); System.out.println("Last Element: " + list.getLast()); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Updating element list.set(1, "Orange"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Removing element list.remove("Apple"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Using LinkedList as a Queue list.addFirst("Grapes"); list.addLast("Pineapple"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating LinkedList for(String fruit : list) { System.out.println(fruit); } } }Output:
[Apple, Banana, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- First Element: Apple Last Element: Banana ------------------------- [Apple, Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- [Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- [Grapes, Orange, Mango, Banana, Pineapple] ------------------------- Grapes Orange Mango Banana Pineapple
Properties of LinkedList Class:
- LinkedList is a linear data structure that stores elements in nodes, where each node contains data and references (links) to the next and previous node.
- LinkedList implements both the
ListandDequeinterfaces, so it can be used as a list, queue, or stack. - LinkedList can store heterogeneous elements if generics are not used.
- It allows storing of duplicate elements.
- It allows storing of null values.
- Insertion order is preserved, meaning elements are retrieved in the same sequence they were added.
- Sorting order is not maintained; explicit sorting is required using
Collections.sort()orlist.sort(). - LinkedList is non-synchronized and not thread-safe.
- Like
ArrayList, it does not guarantee data consistency in multi-threaded environments.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.