ArrayList Class in Java
Introduction
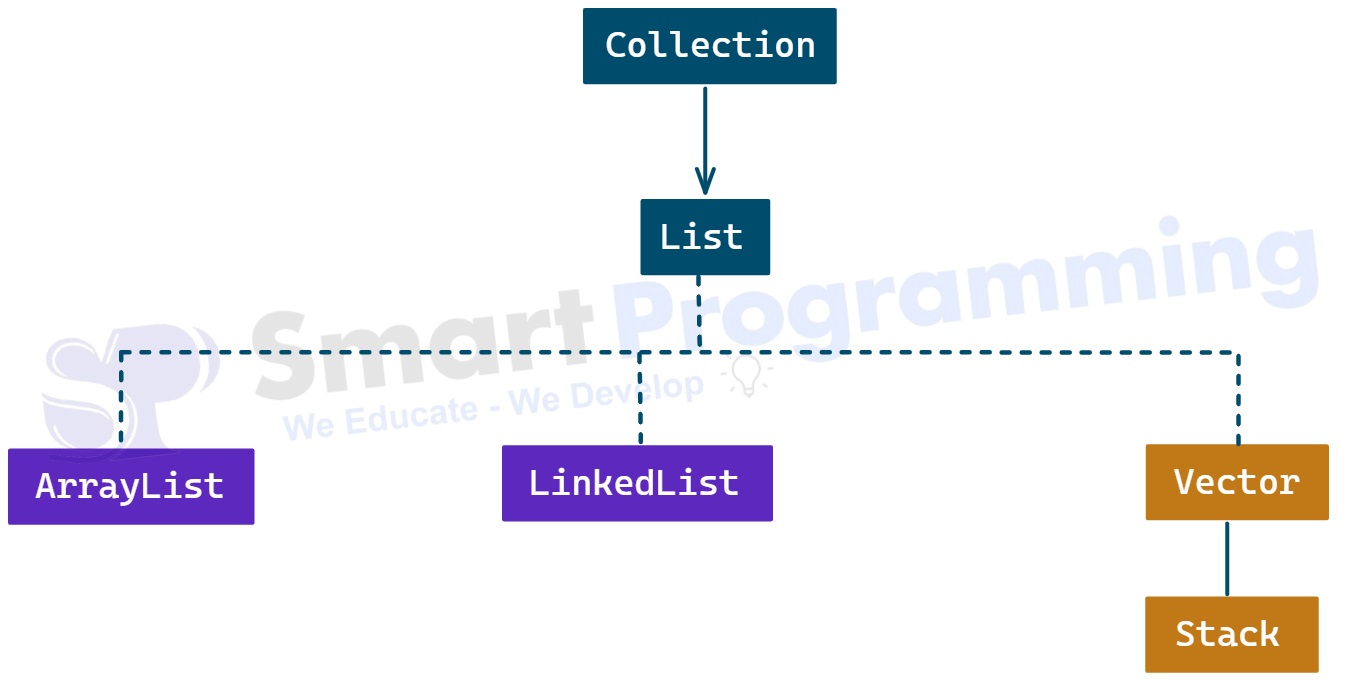
- ArrayList is an implemented class of List interface.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.2 version.
-
Hierarchy:
-
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public class ArrayList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable { // Constructors // Methods // Fields }- ArrayList implements the
RandomAccessmarker interface to indicate efficient indexed access. - It provides fast random access using
get(index)due to the underlying array structure.
- ArrayList implements the
-
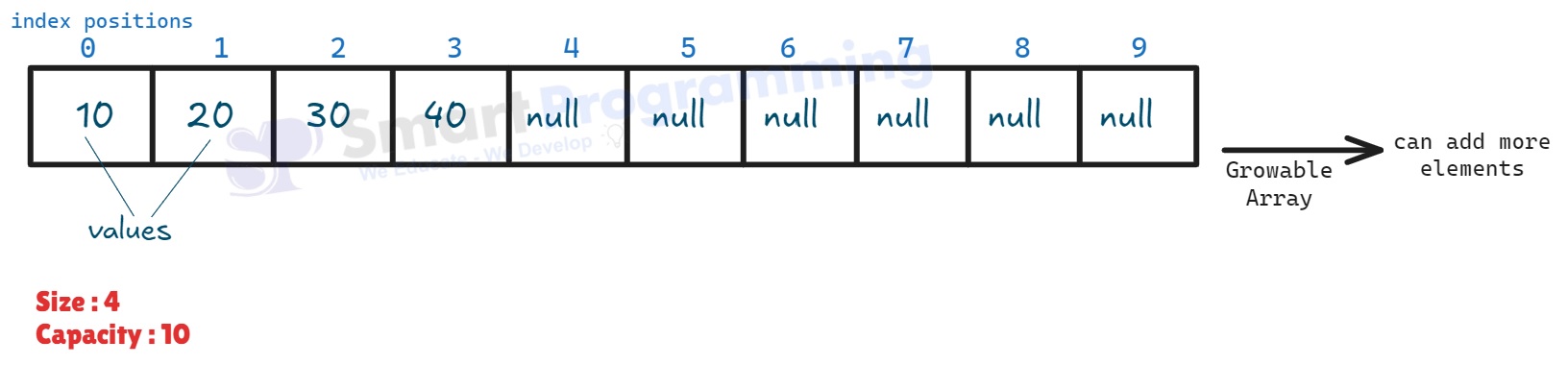
ArrayList is a resizable (dynamic) array in Java that can grow or shrink in size automatically.
Constructors of ArrayList Class
-
Below are the constructors defined in the
ArrayListclass:
| Sr. No. | Constructor | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ArrayList() |
Constructs an empty ArrayList with default initial capacity (10). |
| 2 | ArrayList(int initialCapacity) |
Constructs an empty ArrayList with the specified initial capacity. |
| 3 | ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) |
Constructs an ArrayList containing the elements of the specified collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's iterator. |
Methods of ArrayList Class
-
Below are the methods defined specifically in the
ArrayListclass:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) |
Increases the capacity of the ArrayList, if necessary, to ensure it can hold at least the number of elements specified. |
| 2 | void trimToSize() |
Trims the capacity of this ArrayList instance to be equal to its current size, reducing memory usage. |
Note :
-
ArrayListinherits all the methods ofListandCollectioninterface.
Program :
-
In below program, we are directly using
ArrayListclass. -
import java.util.ArrayList; public class ArrayListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // Adding elements list.add("Apple"); list.add("Banana"); list.add("Mango"); list.add("Banana"); // duplicate allowed System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Accessing element System.out.println("Element at index 2: " + list.get(2)); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Updating element list.set(1, "Orange"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Removing element list.remove("Apple"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating ArrayList for(String fruit : list) { System.out.println(fruit); } } }Output:
[Apple, Banana, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- Element at index 2: Mango ------------------------- [Apple, Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- [Orange, Mango, Banana] ------------------------- Orange Mango Banana
Properties of ArrayList Class:
- ArrayList is an index-based data structure, which means the first element is inserted at
index 0. - ArrayList can store different data types or heterogeneous elements if generics are not used.
- We can store duplicate elements in the ArrayList.
- We can store null values in the ArrayList.
- ArrayList follows the insertion order, meaning elements are retrieved in the same sequence they were added.
- ArrayList does not follows the sorting order; sorting must be done explicitly using
Collections.sort()orlist.sort(). - ArrayList is non-synchronized; not thread-safe for concurrent modifications.
- ArrayList does not guarantee for data consistency.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.