List Interface in Java
Introduction
- List is the child interface of the Collection interface.
-
It is present in the
java.utilpackage. - It was introduced in JDK 1.2 version.
-
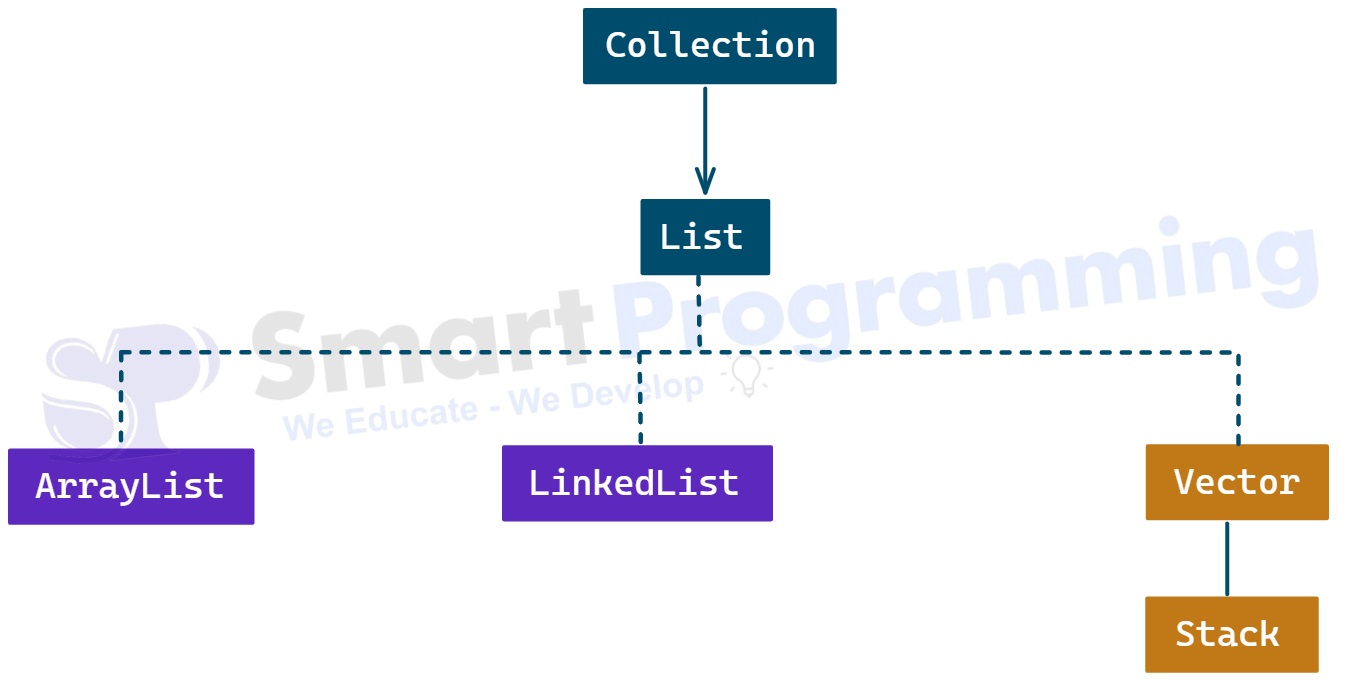
Hierarchy of List Interface:
-
- List is an ordered collection (also known as a sequence) and thus its elements can be accessed using index positions (like arrays).
-
Syntax :-
package java.util; public interface List<E> extends Collection{ // Methods (abstract) }
Methods of List Interface:
-
Below are the methods defined specifically in the
Listinterface:
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | void add(int index, E element) |
Inserts an element at the specified index. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) to the right. |
| 2 | boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) |
Inserts all elements from another collection starting at the specified index. Shifts existing elements to the right. |
| 3 | E get(int index) |
Returns the element at the specified index. |
| 4 | E set(int index, E element) |
Replaces the element at the specified index with the given element and returns the previous element. |
| 5 | E remove(int index) |
Removes and returns the element at the specified position. |
| 6 | int indexOf(Object o) |
Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if not found. |
| 7 | int lastIndexOf(Object o) |
Returns the index of the last occurrence of the specified element, or -1 if not found. |
| 8 | ListIterator<E> listIterator() |
Returns a ListIterator to traverse the list in both forward and backward directions. |
| 9 | ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) |
Returns a ListIterator starting from the specified index. |
| 10 | List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) |
Returns a view of the portion of this list between fromIndex (inclusive) and toIndex (exclusive). Changes in the sublist are reflected in the original list. |
| 11 | static <E> List<E> of(E... elements) |
Returns an unmodifiable list containing the specified elements. (Added in Java 9) |
| 12 | static <E> List<E> copyOf(Collection<? extends E> coll) |
Returns an unmodifiable list containing the elements of the given collection. (Added in Java 10) |
Note :
- List defines what operations a list should support (contract), such as add(), get(), remove(), etc. But it does not define how those operations are performed.
Program :
-
In below program, we are using
Listimplemented class i.e.ArrayList. -
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ListDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { Listlist = new ArrayList<>(); // Adding elements list.add("Java"); list.add("Python"); list.add("C++"); list.add("Java"); // duplicate allowed // Accessing elements System.out.println("Element at index 1: " + list.get(1)); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Updating element list.set(2, "C#"); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Removing element list.remove(0); System.out.println(list); System.out.println("-------------------------"); // Iterating list for(String lang : list) { System.out.println(lang); } } } Output:
Element at index 1: Python ------------------------- [Java, Python, C#, Java] ------------------------- [Python, C#, Java] ------------------------- Python C# Java
Properties of List Interface:
- List is an index-based data structure; the first element is stored at
index 0. - List can store heterogeneous elements if used without
generics, but withgenericsit stores only homogeneous elements of the specified type. - List allows duplicate elements.
- List can store null values.
- List maintains insertion order, meaning elements are retrieved in the same order they are inserted.
- List does not sort elements automatically; sorting must be done explicitly using
Collections.sort()orlist.sort().
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.