Working of ArrayList in Java
Introduction
-
Before understanding the working of
ArrayList, please note the following points:-
ArrayListinternally uses a dynamic array (Object[] elementData) to store its elements. -
Size → Represents the number of elements currently present in the
ArrayList. - Capacity → Indicates the total number of elements that the internal array can hold without resizing.
-
Steps of Working of ArrayList:
-
Below are the steps explaining how
ArrayListworks internally:-
Creation of ArrayList:
-
We create a new
ArrayListas follows:
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); -
A new
ArrayListobject is created with an initial capacity of 10 and a size of 0. This means it can hold up to 10 elements initially, but no elements have been added yet.
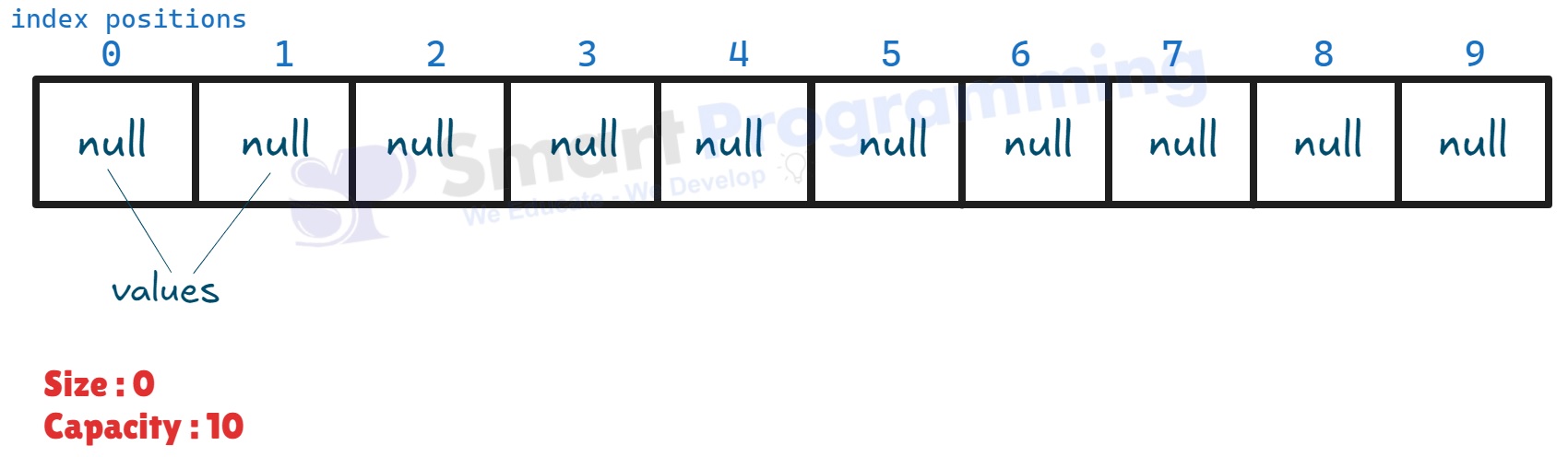
-
We create a new
-
Adding Elements:
-
We add elements using the
add()method:
list.add(10);
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40); -
After adding elements, the size increases and elements are stored in the internal array:
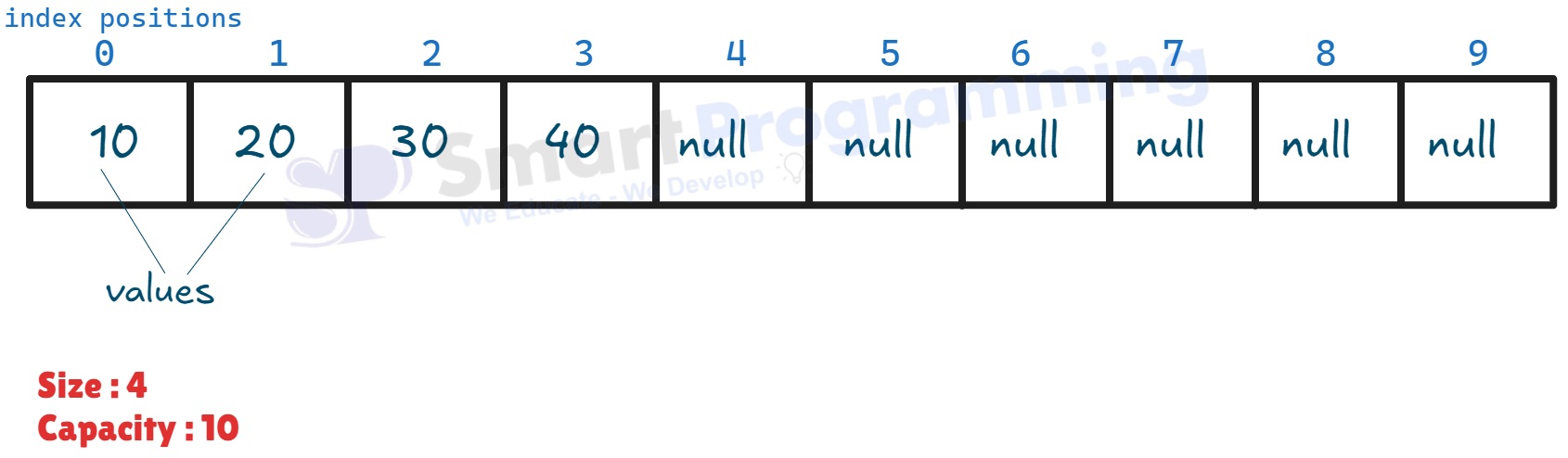
-
We add elements using the
-
When Capacity is Full:
-
When we continue adding elements until size = capacity (size = 10), the internal array becomes fully occupied:
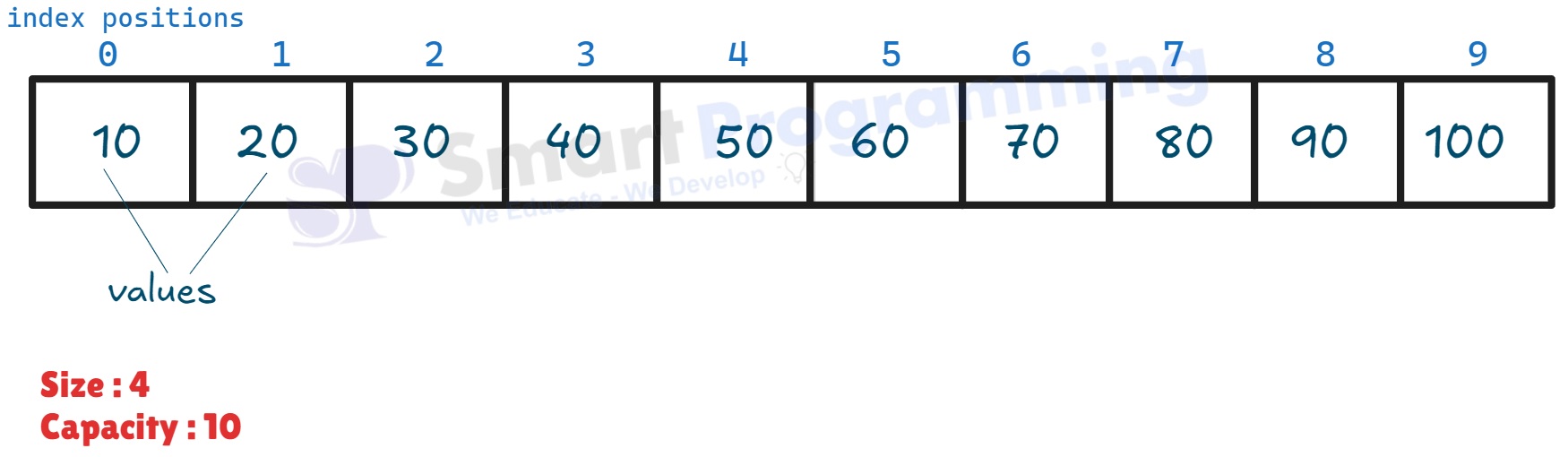
-
If we add one more element (e.g.,
list.add(110)), theArrayListautomatically resizes.
-
When we continue adding elements until size = capacity (size = 10), the internal array becomes fully occupied:
-
Resizing Formula and Copying:
-
The new capacity is calculated using the formula:
newCapacity = (oldCapacity * 3) / 2 + 1 -
Example:
oldCapacity = 10
newCapacity = (10 * 3) / 2 + 1 = 16 - A new internal array of capacity = 16 is created, and all existing elements are copied into the new array. The new element is then added at the next available index.
-
The reference variable of the
ArrayListnow points to the new array, while the old array becomes unreferenced and eligible for garbage collection.
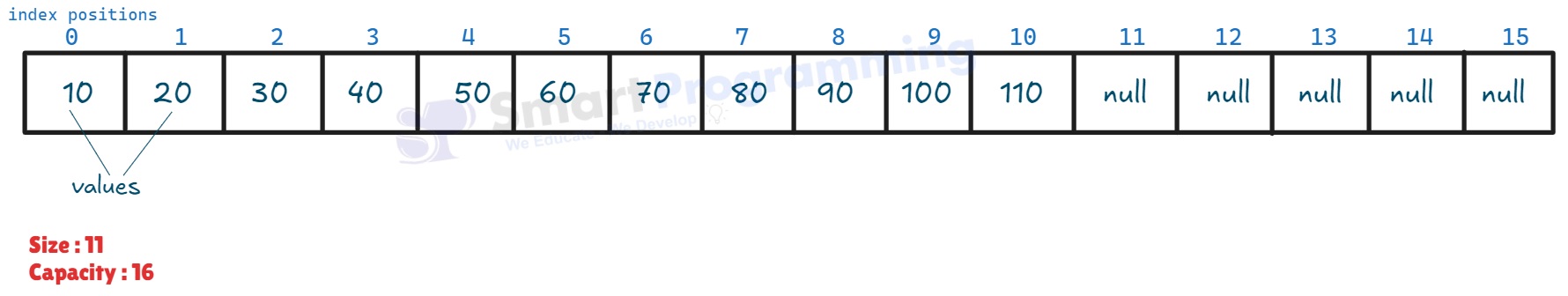
-
The new capacity is calculated using the formula:
-
Creation of ArrayList:
Important Points:
-
There is no direct method to find the capacity of an
ArrayList. We can only obtain the current size usinglist.size(). -
ArrayListallows duplicate elements and null values.
ArrayList is Good for:
-
Accessing elements by index (
get(int index)):- Very fast compared to LinkedList because elements are stored in a contiguous array.
-
Updating elements by index (
set(int index, E element)):- Provides direct replacement in the underlying array without shifting other elements.
-
Adding elements at the end (
add(E e)):- Usually just places the element in the next empty slot, making it very efficient.
-
Iterating through elements:
- Cache-friendly because data is stored in continuous memory blocks.
ArrayList is Not Good for:
-
Inserting elements in the middle or beginning (
add(int index, E element)):- Requires shifting of all subsequent elements, which slows down performance.
-
Removing elements from the middle or beginning (
remove(int index)):- Needs to shift elements left to fill the gap, making it less efficient.
-
Frequent resizing when capacity is exceeded:
- Creates a new array and copies old elements, which is costly if done often.
-
Searching for elements (
contains,indexOf):- Requires checking each element one by one, since there’s no built-in hashing or sorting.
Summary Table:
| Operation | Performance | Complexity |
|---|---|---|
Access by index (get) |
Very Fast | O(1) |
Update by index (set) |
Very Fast | O(1) |
Add at end (add) |
Fast | O(1) amortized |
Insert in middle/start (add(i)) |
Slow | O(n) |
Remove by index/value |
Slow | O(n) |
Search (contains, indexOf) |
Slow | O(n) |
Iteration |
Fast | O(n) but cache-friendly |
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



