Spring Container
What is Spring Container?
- Spring Container is the "Core Part" or say "Heart " of the Spring Framework which is responsible for creation, configuration and managing the lifecycle of beans (objects)
- It follows the IoC (Inversion of Control) principle by injecting dependencies automatically, reducing tight coupling between components.
- It reads configuration metadata (XML, annotations, or Java config) to know how to manage the beans.
Responsibilities of Spring Container
Below are some key responsibilities of the Spring Container :-1. Bean Creation and Initialization :
- Spring Container is responsible to create and initialize the beans (objects) defined in the Spring configuration.
2. Bean Configuration Handling :
- Spring Container is responsible to loads the configuration from XML, annotations or Java-based configuration files.
3. Bean Lifecycle Management :
- Spring Container is responsible to handle the complete bean lifecycle, including initialization (@PostConstruct) and destruction (@PreDestroy).
4. Beans Scope Management :
- Spring Container supports different bean scopes (e.g., singleton, prototype) to control the lifecycle and usage of beans.
5. Dependency Injection (DI) :
- Spring Container injects the dependencies between objects, ensuring loose coupling.
6. AOP (Aspect-Oriented Programming) Support :
- Spring Container allows cross-cutting concerns like logging and security to be modularized through aspects.
7. Integration with Other Technologies :
- Spring Container supports integration with databases, messaging services and web frameworks.
8. Internationalization (I18N) Support :
- Spring Container supports Internationalization (i18n), enabling applications to present messages, formats, and resources in multiple languages, making it adaptable for users across different regions.
9. Environment Management :
- Spring Container provides support for property sources and profiles for environment-specific configurations.
10. Bean Post-Processing :
- Spring Container allows the use of BeanPostProcessor to modify bean instances before and after initialization.
Working of Spring Container
Below is the diagram showing the working of Spring Container :-
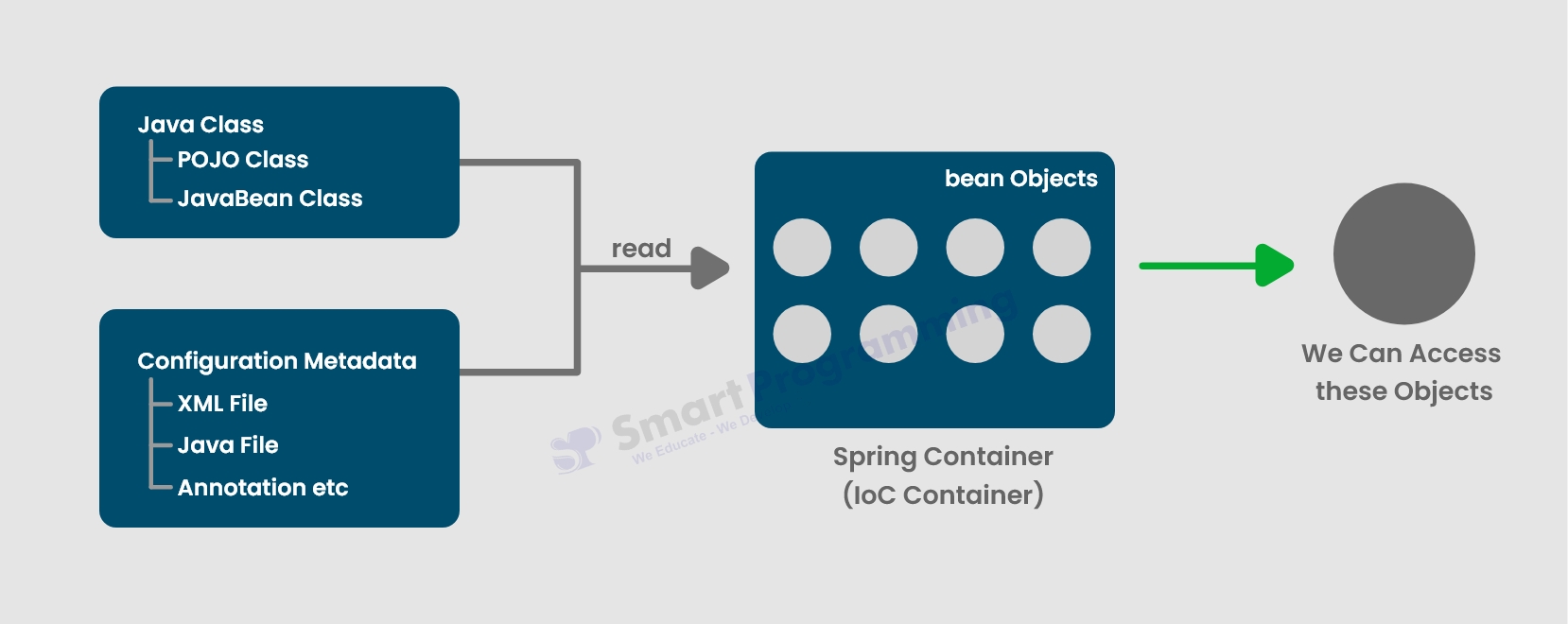
Below is the explanation :-
- Java Classes : Java classes (like POJO's & JavaBean's) are used to create simple Java objects that represent components or beans in the application. They contain business logic, but are independent of the Spring framework.
-
Configuration Metadata : Configuration files (like XML files, Java-based configuration classes or annotations) provide the metadata which specifies:
- Which classes to instantiate as beans.
- How beans are wired together (dependency injection)
- The lifecycle and scope of each bean.
-
Spring Container :
- The Spring Container reads the configuration metadata and scans the specified classes.
- It then instantiates and configures the required beans, applying dependency injection as specified.
- The container manages the lifecycle of these beans, creating them as needed and handling initialization, dependencies, and destruction.
- Bean Objects : The container creates and stores instances of beans based on the configuration. These are the fully managed objects that can be injected or retrieved throughout the application.
- Accessing Beans : Once created, these bean objects are accessible throughout the application. They can be injected into other components or accessed on demand using dependency injection or by looking up beans from the container.
Types of Spring Container
There are 2 types of Spring Container :-
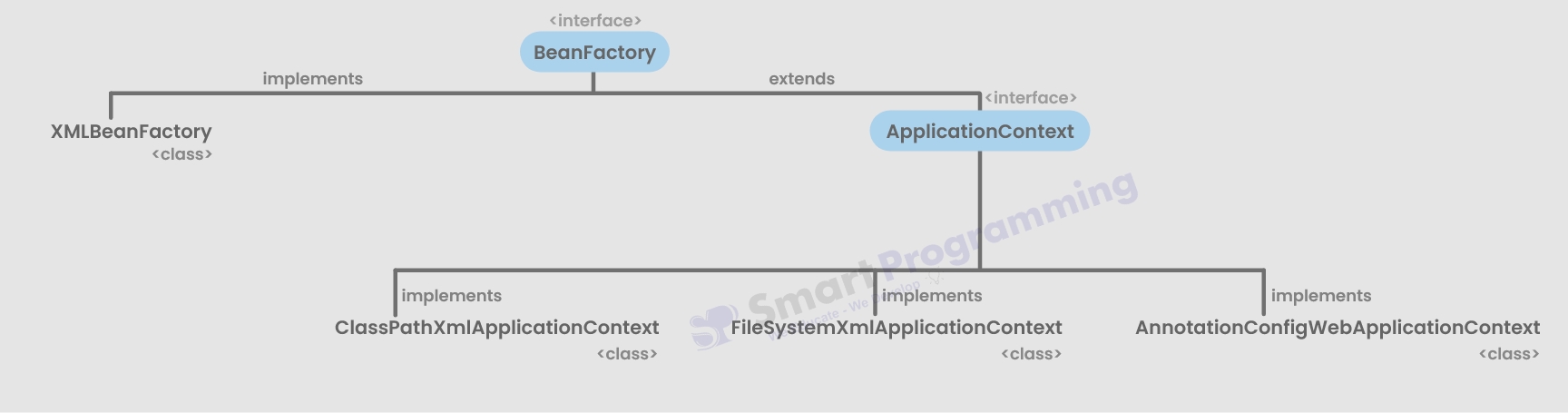
1. BeanFactory
2. ApplicationContext
-
"BeanFactory" Container:
- BeanFactory Container is lightweight and basic IoC container.
- BeanFactory Container creates the beans when they are requested and this concept is known as Lazy Initialization.
- BeanFactory Container is suitable for simple applications where performance is crucial and resources are limited.
-
"ApplicationContext" Container
- ApplicationContext Container is more advanced version of BeanFactory with extra features like AOP & Internationalization (I18N) support, event propagation, declarative mechanisms etc
- ApplicationContext Container creates the beans during container startup and this concept is known as Eager Initialization.
- ApplicationContext Container is suitable for Enterprise-level applications that require more features, such as transactions, events, and AOP.
Note: BeanFactory is an "old" Spring Container and ApplicationContext is "new" Spring Container and provides many extra features so we should always use ApplicationContext in real world projects.
Interview Question : What is Difference between BeanFactory & ApplicationContext ?
Click Here for answer
Hierarchy of Spring Container's
Below is the hierarchy of Spring Containers :-
- Click Here to read "BeanFactory" more deeply
- Click Here to read "ApplicationContext" more deeply
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.