Push Local Changes to Remote Repository -
Introduction
-
git pushcommand is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket). - It transfers your committed changes from the current local branch to a branch on the remote repository.
- It ensures that your team or remote server has the latest version of your code.
-
It is commonly used after making and committing changes using
git commit.
How to use git push ?
- Open the Git terminal (or command prompt) and navigate to the project folder where your Git repository is initialized.
-
Make sure that :-
-
You have already committed your changes using:
-
git commitCommand
-
-
You have added the remote repository using:
-
git remote add origin https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.gitCommand
-
-
You have checked that local and remote branch name are same, if not same then change it using:
-
git branch -M mainCommand
-
-
You have already committed your changes using:
-
Now run the git push command:
-
Syntax :
git push origin <branch-name> -
Example :
git push origin main
-
Syntax :
-
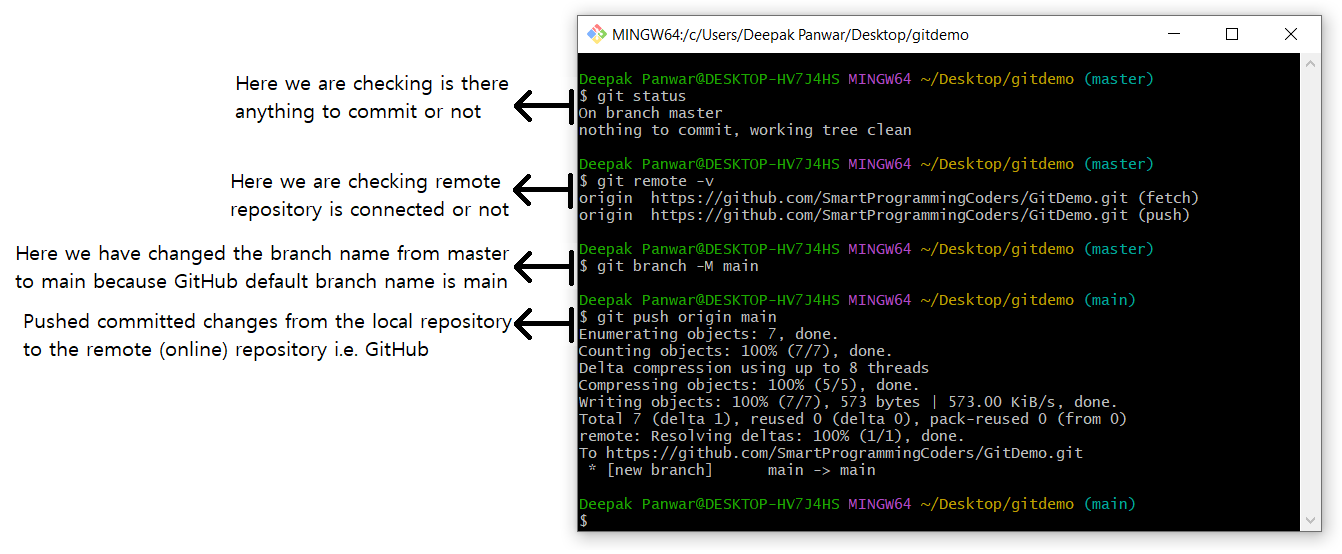
The commands will show the following output:
-
Different ways to use git push ?
-
Basic Push to Remote Repository::
- Push committed changes from your local branch to a remote repository.
-
Syntax :
-
git push origin <branch-name>
-
-
Example:
-
git push origin main
-
-
Push and Set Upstream (Track Remote Branch):
- Sets the remote branch as the default upstream for your local branch.
-
Syntax:
-
git push -u origin <branch-name>
-
-
Example:
-
git push -u origin main
-
-
Note : After this, you can simply run
git pushnext time.
-
Push All Branches:
- Push all local branches to the remote repository.
-
Example:
-
git push --all origin
-
-
Push Tags:
- If you’ve created Git tags and want to push them:
-
Example:
- git push origin --tags
-
Force Push:
- Used to overwrite remote history with local changes (⚠️ use with caution).
-
Example:
-
git push --force -
git push origin main --force
-
-
Push to a Different Remote:
-
If your remote is named something other than
origin, specify it: -
Syntax:
-
git push my-remote-name <branch-name>
-
-
If your remote is named something other than
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.