Cloning a Git Repository - git clone
Introduction
-
git clonecommand is used to create a copy of an existing Git repository from a remote server (like GitHub, GitLab) to your local machine. - It initializes a new local repository and automatically sets up a remote connection to the source repository.
-
Features of
git clone:- It will download all files, commit history, branches and tags from the remote repository.
- It will creates a new folder with the same name as the repository (unless you specify a different name).
- It will lnks your local repository to the remote source, making it easy to pull updates.
How to use git clone ?
- Open the Git terminal (or command prompt) and navigate to the project folder where your Git repository is initialized.
-
Make sure that:
- You have the remote repository URL (for example, from GitHub). In previous tutorial we have pushed one repository on GitHub.
-
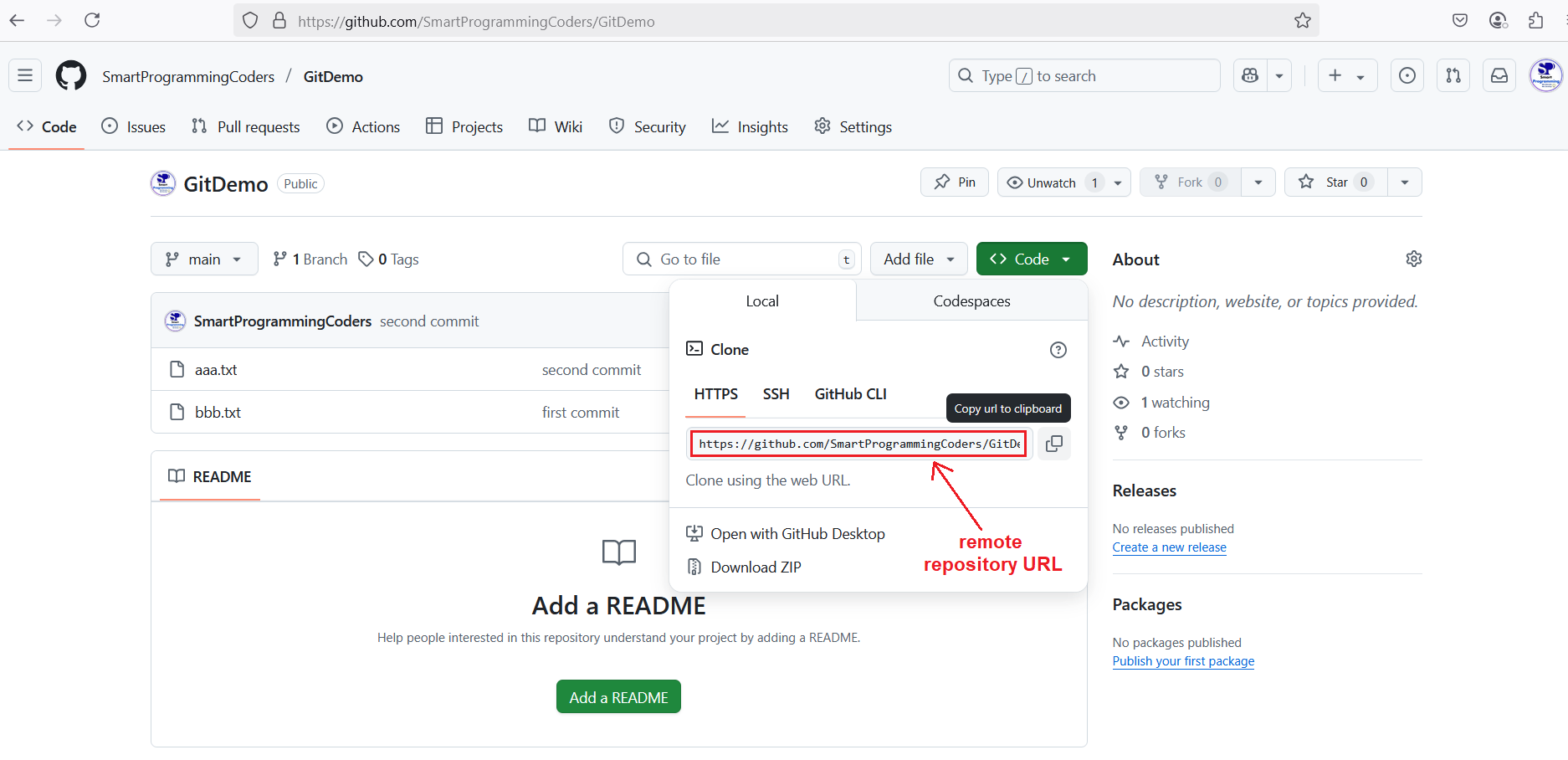
-
Now run the
git clonecommand:-
Syntax :
git clone <remote-repo-URL> -
Example :
git clone https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git
-
Syntax :
-
The command will show the following:
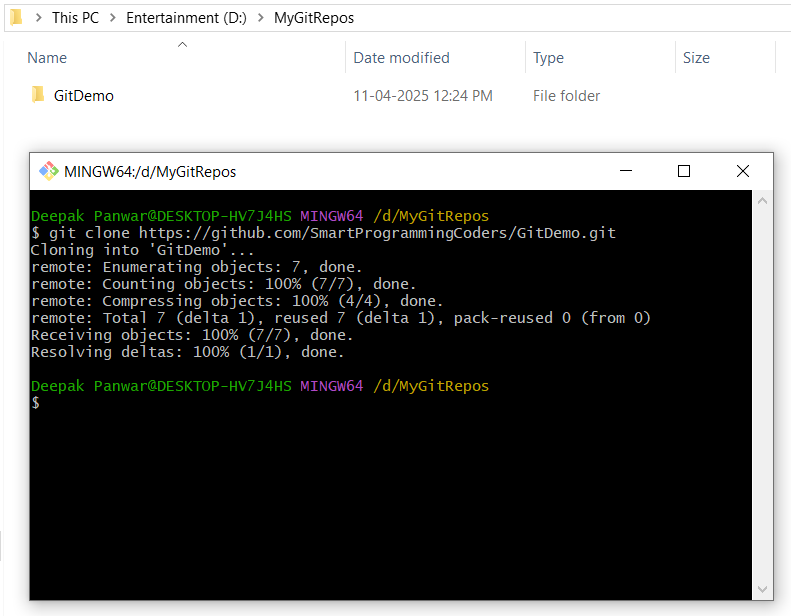
-
Here, we have cloned the GitHub repository from the URL
https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.gitto our local machine using thegit clonecommand. - This creates a local copy of the repository, allowing us to work on the project locally while staying connected to the remote repository on GitHub.
Different ways to use git clone ?
-
Cloning Basic Repo:
-
Syntax:
-
git clone <repository-url>
-
-
Example:
-
Clone from Online Repo:
git clone https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git -
Clone from Local Repo (less preferred):
git clone "C:\Users\Deepak Panwar\Desktop\gitdemo"
-
Clone from Online Repo:
-
Syntax:
-
Cloning into a Specific Directory:
-
Syntax:
-
git clone <repository-url> <custom-directory-name>
-
-
Example:
git clone https://github.com/SmartProgrammingCoders/GitDemo.git my-local-repo
-
Syntax:
-
Cloning into a Specific Directory:
-
Syntax:
-
git clone <repository-url> <custom-directory-name>
-
-
Example:
-
git clone https://github.com/username/repo-name.git my-local-repo
-
-
Syntax:
-
Cloning with Specific Branch:
-
By default,
git clonefetches the default branch (usuallymainormaster). -
To clone a specific branch, syntax is:
-
git clone -b <branch-name> <repository-url>
-
-
Example:
-
git clone -b develop https://github.com/username/repo-name.git
-
-
By default,
-
Cloning with Limited History:
- If you want to save time and bandwidth, clone only recent commits:
-
Syntax:
-
git clone --depth <number> <repository-url>
-
-
Example:
-
git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/username/repo-name.git(clones only the latest commit)
-
-
Cloning via SSH:
- If you have SSH access configured, you can use the SSH URL:
-
Example:
-
git clone git@github.com:username/repo-name.git
-
- Faster and more secure for private repositories.
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



