Merging Changes in Git Repository - git merge
Introduction
-
git mergecommand is used to update your current local branch with changes from the remote branch (like origin/main). -
Here, you are using this command after running
git fetch, which downloads the latest changes from the remote server. -
This method gives you more control than
git pull, because you can see the changes first before merging them into your branch.
NOTE :
-
The
git mergecommand is also commonly used to combine changes between local branches, for example, merging a feature branch into main during development. - To learn more about merging local branches, click here to view the Git Merge (Local Branches) section.
How to use git merge ?
-
Fetch Changes :-
-
In previous
git fetchtutorial, we have retrieved the latest changes from the GitHub repository.
- Click Here to read previous tutorial.
-
Below are the commands with output:

-
In previous
-
Merge Changes in Another Local Repository :-
- Now, in another local directory where we have cloned the repository, we will merge the latest changes from the original location.
-
Syntax :
-
git merge FETCH_HEAD
-
-
The command will show the following output:
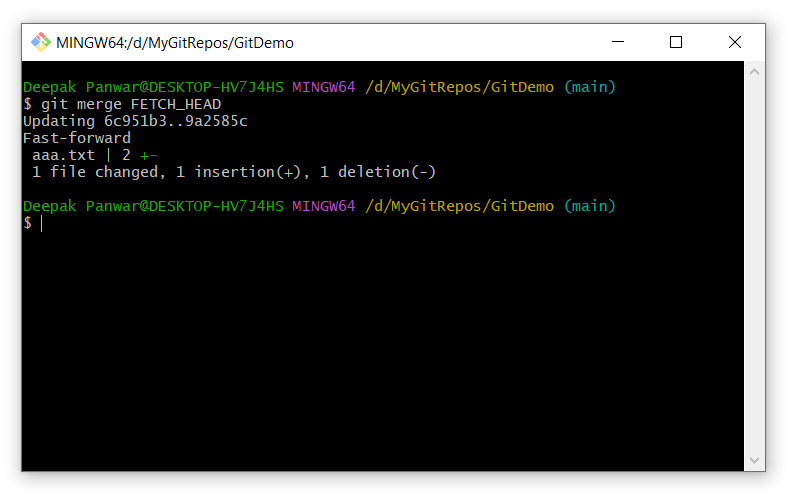
This command merge the latest changes from the specified repository.
NOTE :
- Use FETCH_HEAD only after fetching changes when merging manually.
-
If you are merging a branch directly, you specify the branch name instead:
-
git merge <branch-name>
-
-
If you are working with a remote repository,
git pull(which is git fetch + git merge) automatically merges fetched changes.
Different ways to use git merge ?
-
Merging Changes Locally:
-
Syntax :
-
git merge FETCH_HEAD
-
-
Example:
-
git merge FETCH_HEAD
-
-
Merges fetched changes from another local repository after using
git fetch.
-
Syntax :
-
Merging a Local Branch into the Current Branch:
-
Syntax :
-
git merge <branch-name>
-
-
Example:
git merge feature-branch
-
Merges
feature-branchinto the currently checked-out branch.
-
Syntax :
-
Abort a Merge in Case of Conflict:
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --abort
-
- If conflicts occur during merging, this command cancels the merge process.
-
Syntax :
-
Merging After Fetching from a Remote Repository (Most Common):
-
Syntax :
-
git merge origin/<branch-name>
-
-
Example :
-
git merge origin/main
-
-
Merges the latest changes from the remote
mainbranch into your local branch after fetching updates.
-
Syntax :
-
Fast-Forward Merge (If No Diverging Changes Exist) (Commonly Used) :
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --ff-only <branch-name>
-
-
Exmaple :
-
git merge --ff-only origin/main
-
- Merges the remote branch only if no conflicting changes exist.
-
Syntax :
-
Squash Merge (Combine Multiple Commits into One Before Merging) (Commonly Used for Clean History) :
-
Syntax :
-
git merge --squash <branch-name>
-
-
Example :
-
git merge --squash feature-branch
-
-
Combines all commits from
feature-branchinto a single commit before merging.
-
Syntax :
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



