Selection Sort Algorithm in DSA (Java)
Introduction
- Selection Sort is a simple comparison-based sorting algorithm used to arrange elements in ascending or descending order.
- It selects the minimum (or maximum) element from the unsorted part of the array and places it at the correct position in the sorted part.
- This process continues until the entire array is sorted.
-
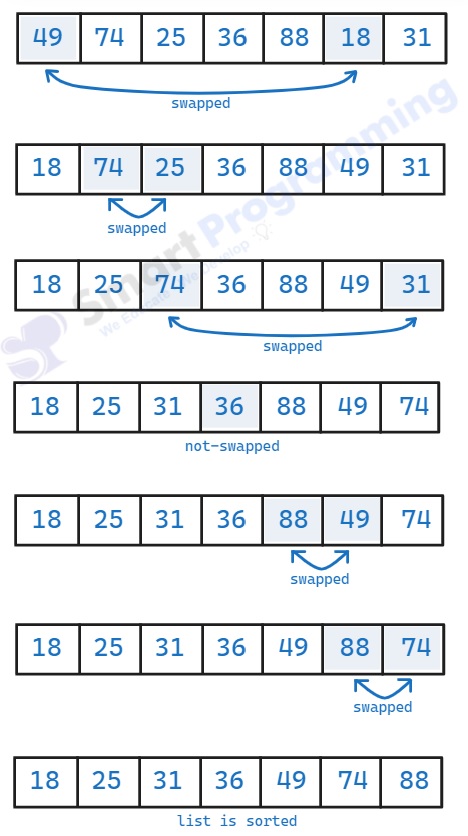
Logic / Steps (Simple):
- Start from the first element and assume it is the minimum.
- Compare it with the remaining elements to find the actual minimum in the unsorted part.
- Swap the found minimum element with the first element of the unsorted part.
- Move the boundary of the sorted part by one element and repeat the process for the rest of the array.
- Continue until the entire array is sorted.
-
Program:
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {49, 74, 25, 36, 88, 18, 31}; int n = arr.length; // Selection Sort Algorithm for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) { int minIndex = i; // Find the minimum element in unsorted part for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) { if (arr[j] < arr[minIndex]) { minIndex = j; } } // Swap the found minimum element with the first element int temp = arr[minIndex]; arr[minIndex] = arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } // Print sorted array System.out.print("Sorted Array: "); for (int num : arr) { System.out.print(num + " "); } } }Output:
Sorted Array: 18 25 31 36 49 74 88
Important Points to Note :-
- Selection Sort is a simple comparison-based sorting algorithm that repeatedly selects the minimum (or maximum) element from the unsorted part and moves it to the sorted part.
- It is not stable by default (may change the order of equal elements) but can be made stable with modifications.
- It is not adaptive; always performs the same number of comparisons regardless of initial order.
- Selection Sort follows the selection and swapping approach.
- Using a minimum/maximum selection at each iteration reduces the number of swaps compared to Bubble Sort.
-
Time Complexity for Selection Sort:
-
Case Description No. of Comparisons Time Complexity Worst Case Array is in reverse order; all comparisons still required. n(n-1)/2O(n²)Average Case Elements are in random order; all comparisons still required. n(n-1)/2Θ(n²)Best Case Array is already sorted; comparisons still performed, but minimum swaps. n(n-1)/2Ω(n²)
-
-
Space Complexity:
-
O(1)→ only a few variables used; no extra memory needed.
-
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.