Binary Search Algorithm in DSA (Java)
Introduction
- Binary Search is an efficient searching algorithm used to find an element in a sorted array.
- It works on the principle of divide and conquer.
- The array is divided into halves and the search is performed in the relevant half.
-
Logic / Steps (Simple):
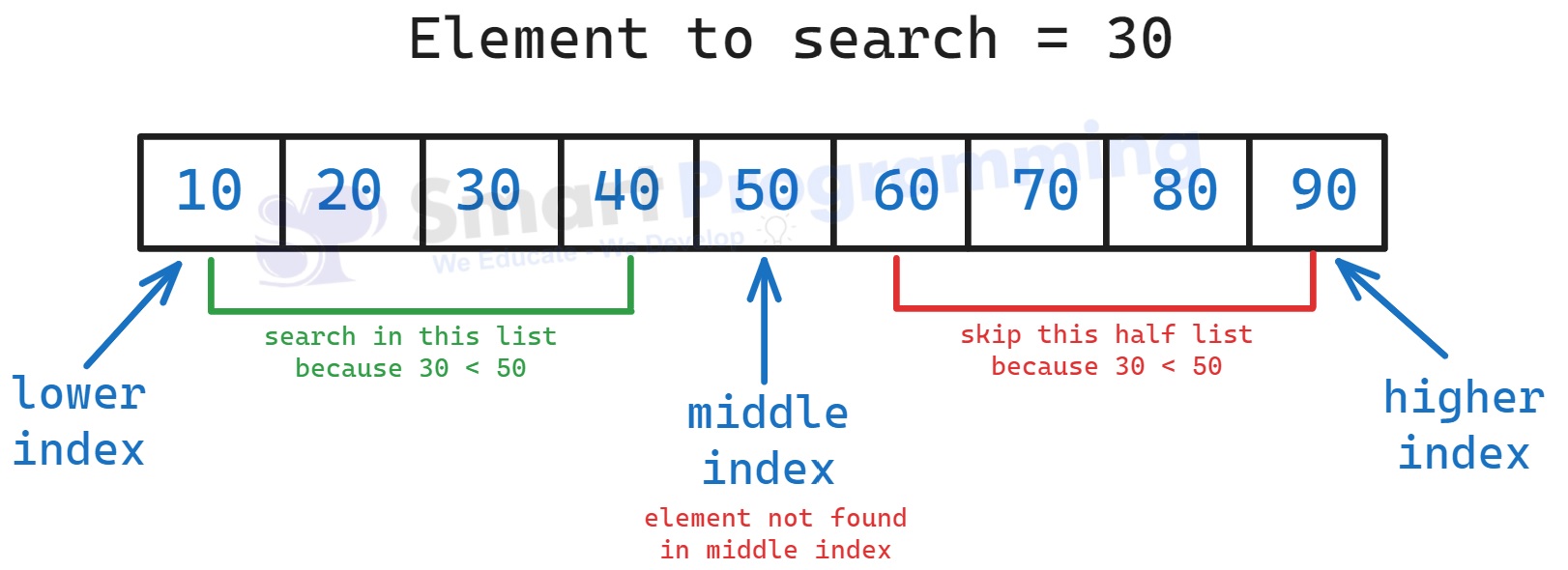
- We divide the array into two halves by finding the middle element.
- If the middle element matches the key, we print its index.
- If the key is smaller than the middle element, we search in the left half, otherwise in the right half.
- Repeat the process until the element is found or the search space becomes empty.
-
Program:
public class BinarySearchExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90}; int element = 30; int li = 0; // low index int hi = arr.length - 1; // high index boolean found = false; while (li <= hi) { int mid = (li + hi) / 2; if (arr[mid] == element) { System.out.println("Element found at index: " + mid); found = true; break; } if (element > arr[mid]) { li = mid + 1; // search in right half } else { hi = mid - 1; // search in left half } } if (!found) { System.out.println("Element not found"); } } }Output:
Element found at index: 2
Important Points to Note :-
- Binary Search is much more efficient than Linear Search, but it works only on sorted arrays.
- Binary Search follows the divide and conquer approach.
-
Time Complexity for Binary Search:
-
Case Description No. of Comparisons Time Complexity Worst Case Element is not present, or found after repeatedly dividing the array until size becomes 1. log₂nO(log n)Average Case Element is found somewhere after a few halvings of the array. log₂nΘ(log n)Best Case Element is found at the first middle position checked. 1Ω(1)
-
-
Space Complexity:
-
O(1)→ only a few variables are used in iterative method; no extra memory needed. -
O(log n)→ in recursive method, due to function call stack usage.
-
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.