Linear Search Algorithm in DSA (Java)
Introduction
- Linear Search is a simple searching technique used to find a particular element in an array or list.
- It checks each element one by one until the desired element is found or the array ends.
- It is also called sequential search.
-
Logic / Steps (Simple):
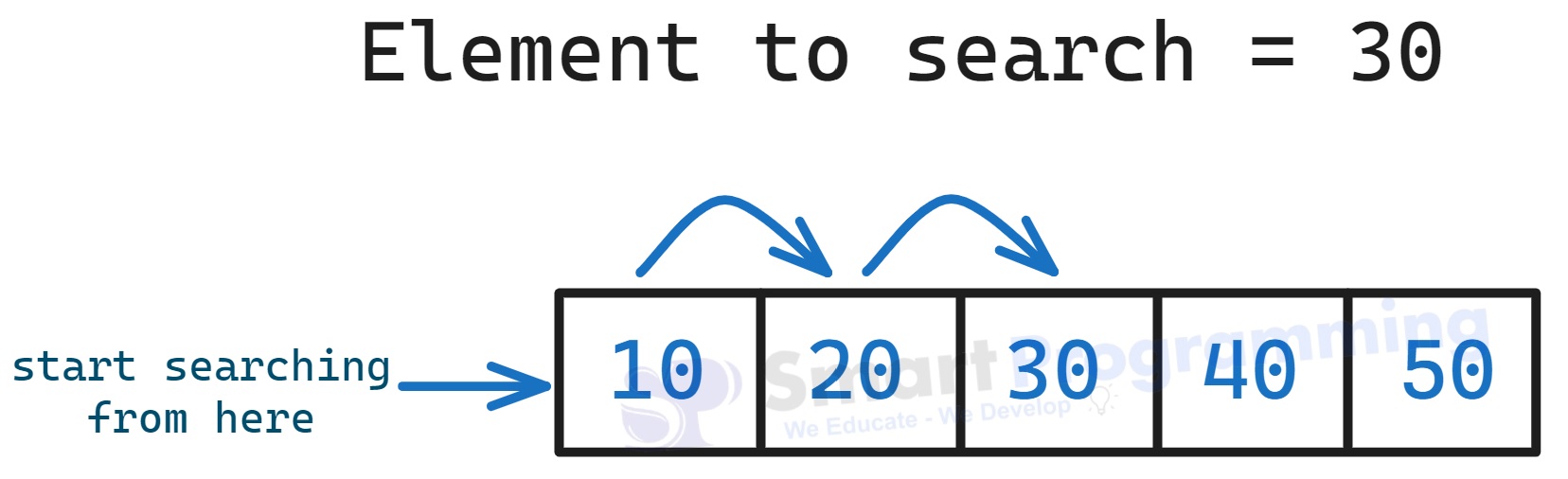
- Start searching from the first element of the array.
- If the element matches, print its index position and stop.
- If not, keep checking the next element until found or array ends. If not found, return -1.
-
Program:
public class LinearSearchExample { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] arr = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; int key = 30; boolean found = false; // Linear search for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { if (arr[i] == key) { System.out.println("Element found at index: " + i); found = true; break; } } if (!found) { System.out.println("Element not found"); } } }Output:
Element found at index: 2
Important Points to Note :-
- Linear Search is simple and easy to implement, but not efficient for large datasets.
- Linear Search can work on unsorted arrays.
-
Time Complexity for Linear Search:
-
Case Description No. of Comparisons Time Complexity Worst Case The element is either at the last position or not present in the array. nO(n)Average Case The element is found somewhere in the middle of the array. n/2Θ(n)Best Case The element is found at the first position. 1Ω(1)
-
-
Space Complexity:
-
O(1)→ only a few variables are used; no extra memory is needed.
-
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.