Writer Classes
Introduction
-
Writeris an abstract class used to write character-oriented data (16-bit Unicode) to output destinations such as files, memory or network connections. -
It is present in the
java.iopackage. -
It provides basic methods like
write()to write single characters, arrays of characters, or strings to output sources. -
Unlike
OutputStreamwhich deals with bytes,Writeris specifically designed to handle characters, making it suitable for text data.
-
Below is the diagram for Writer class hierarchy:
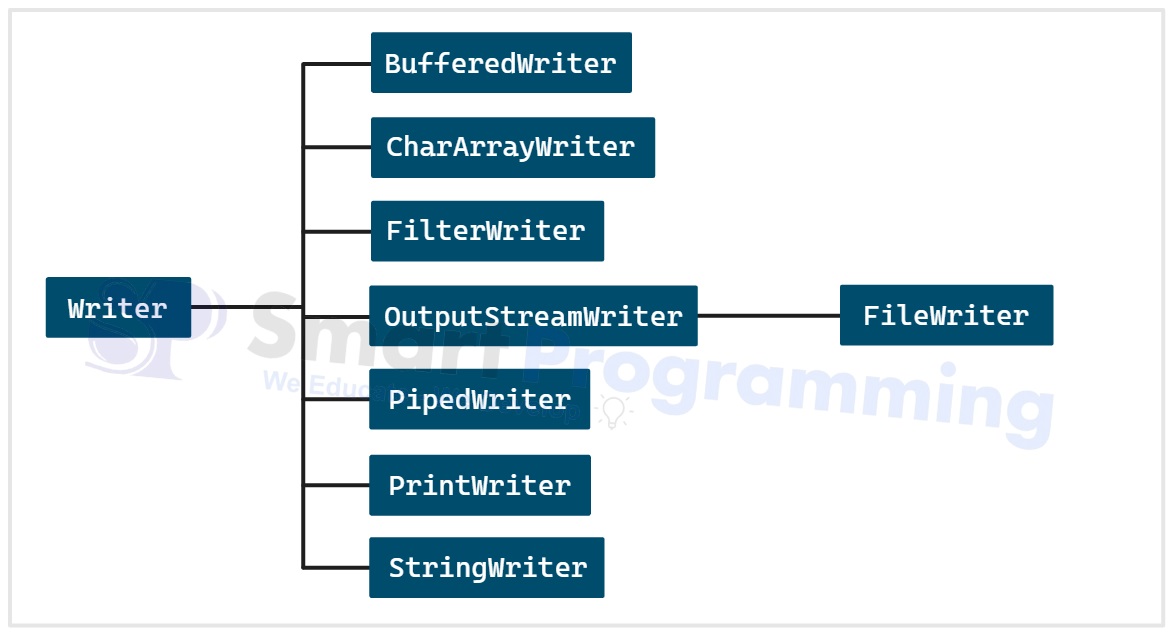
- Each of these subclasses are designed for specific purposes, which are explained below one by one.
1. BufferedWriter
- Description: Writes text to a character output stream efficiently by buffering characters, reducing the number of I/O operations.
- Use in Projects: Commonly used for writing large amounts of text data to files.
-
Example Syntax:
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("file.txt")); bw.write("Hello Java"); bw.close();
2. CharArrayWriter
- Description: Writes characters to a character array, which can be converted to a string or retrieved later.
- Use in Projects: Useful when you need to create strings dynamically or when working with in-memory text data.
-
Example Syntax:
CharArrayWriter caw = new CharArrayWriter(); caw.write("Hello Java"); System.out.println(caw.toString()); caw.close();
3. FilterWriter
- Description: An abstract class for writing filtered character streams. It acts as a base class for subclasses that modify output data.
- Use in Projects: Rarely used directly; extended to implement custom filters.
-
Example Syntax:
// FilterWriter is abstract and cannot be used directly // Example subclass: can be extended for custom filtering
4. OutputStreamWriter
- Description: A bridge between byte streams and character streams. Converts characters into bytes using a specified charset.
- Use in Projects: Commonly used to write characters to byte-oriented destinations (like network sockets).
-
Example Syntax:
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out); osw.write("Hello Java"); osw.close();
5. FileWriter
-
Description: A convenient subclass of
OutputStreamWriterthat is used for writing characters to files. - Use in Projects: Simplifies writing text files without explicitly specifying character encoding (uses platform default).
-
Example Syntax:
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("file.txt"); fw.write("Hello Java"); fw.close();
6. PipedWriter
-
Description: Writes characters to a connected
PipedReader, enabling communication between threads. - Use in Projects: Useful in multithreaded applications for inter-thread data transfer.
-
Example Syntax:
PipedWriter pw = new PipedWriter(); PipedReader pr = new PipedReader(pw); pw.write("Hello from thread"); pw.close(); pr.close();
7. PrintWriter
-
Description: Writes formatted text to a character output stream and provides convenient methods like
print()andprintln(). - Use in Projects: Commonly used for writing text-based logs or console-like output to files.
-
Example Syntax:
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("file.txt"); pw.println("Hello Java"); pw.close();
8. StringWriter
- Description: Writes characters to a string buffer, which can be converted to a string later.
- Use in Projects: Useful for creating text dynamically in memory before saving or processing.
-
Example Syntax:
StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); sw.write("Hello Java"); System.out.println(sw.toString()); sw.close();
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



