Stream API
Introduction
-
Stream API was introduced in Java 8 as part of the
java.util.streampackage. -
Stream API = Stream + API
-
A Stream is a sequence of elements from a data source
(
List,Set,Array) that allows functional operations likefilter,map, andsort, and can run sequentially or in parallel. - API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of predefined classes, interfaces and methods needed to create, manipulate, and process streams efficiently.
-
A Stream is a sequence of elements from a data source
(
-
Uses of Stream API:
- Iterating: Iterate over collections in a clean and concise way (without explicit loops).
-
Filtering: Filter data based on conditions using
filter(). -
Transforming: Transform data using
map()(e.g. converting strings to uppercase, objects to another type). -
Sorting: Sort data easily using
sorted(). -
Collecting: Collect results back into a list, set or map using
collect(). -
Finding: Find results such as
min(),max(),count()oranyMatch()efficiently. -
Reducing: Reduce data to a single value using
reduce()(e.g., sum, multiplication). -
Parallel Processing: Process data in parallel using
parallelStream()for faster performance on multicore systems. - Code Benefits: Makes code shorter, easier to maintain, and closer to functional programming style.
Important classes & interfaces in Stream API:
-
Some important classes and interfaces in Stream API are as follows:
S.No Class / Interface Important Methods Description 1 Stream(Interface)filter(),map(),distinct(),sorted(),limit(),skip(),forEach()Represents a sequence of elements supporting sequential and parallel aggregate operations. 2 IntStream(Interface)range(),rangeClosed(),sum(),average(),min(),max()Specialized stream for handling int values efficiently. 3 LongStream(Interface)range(),rangeClosed(),sum(),average(),min(),max()Specialized stream for handling long values efficiently. 4 DoubleStream(Interface)of(),average(),sum(),min(),max(),summaryStatistics()Specialized stream for handling double values efficiently. 5 Collectors(Class)toList(),toSet(),toMap(),joining(),groupingBy(),partitioningBy()Provides static methods to accumulate elements from a stream into collections or other forms. 6 Optional(Class)isPresent(),get(),orElse(),ifPresent(),map(),flatMap()Represents a container object which may or may not contain a non-null value, used for safe handling of nulls. 7 BaseStream(Interface)iterator(),spliterator(),close(),parallel(),sequential()Parent interface for all streams providing common operations like closing and switching between parallel/sequential.
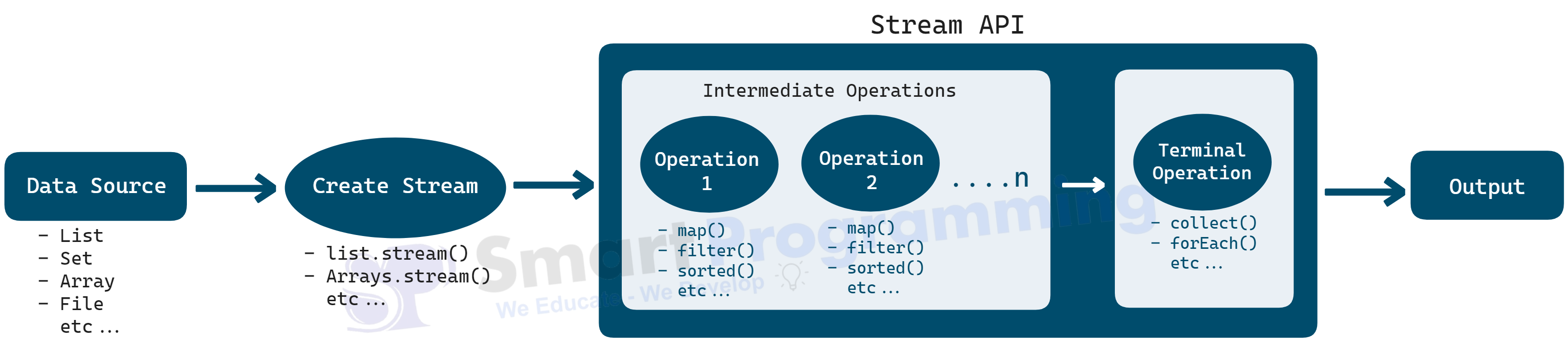
Working of Streams
-
Below is the diagram represeing the working of Stream API:
-
Explanation:
-
Data Source
-
The data comes from collections like
List,Set, or arrays. -
Example:
List<Integer> numbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
-
The data comes from collections like
-
Create Stream
-
Convert the data source into a stream using
.stream()orArrays.stream(). -
Example:
Stream<Integer> stream = numbers.stream();
-
Convert the data source into a stream using
-
Intermediate Operations (Lazy operations)
- Used to transform or filter data.
- They don’t execute immediately — they just build a pipeline.
-
Example:
stream = stream .filter(n -> n % 2 == 0) // keep even numbers .map(n -> n * n); // square them -
Common intermediate operations:
filter(),map(),sorted(),distinct(),limit()
-
Terminal Operation (Triggers execution)
- This step processes the data and produces a result or a side effect.
-
Example:
stream.forEach(System.out::println); // prints result -
Common terminal operations:
collect(),forEach(),reduce(),count(),toArray()
-
Output
- Final result is either a collection, a single value, or just printed output.
-
Data Source
Programs:
-
Program 1: (Get all even numbers from list and square it)
import java.util.List; import java.util.Arrays; public class MainApp1 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 1️⃣ DATA SOURCE Listnumbers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 2️⃣ CREATE STREAM from the data source numbers.stream() // 3️⃣ INTERMEDIATE OPERATIONS (lazy) .filter(n -> n % 2 == 0) // filter: keep only even numbers .map(n -> n * n) // map: square the even numbers // 4️⃣ TERMINAL OPERATION (triggers execution) .forEach(System.out::println); // print each result // 5️⃣ OUTPUT // 4 (2 * 2) // 16 (4 * 4) } } Output:
4 16
-
Program 2: (Filter Names Starting with 'd', Convert to Uppercase, and Sort Using Stream API)
import java.util.List; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class MainApp2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Listnames = Arrays.asList("diksha", "rahul", "amit", "deepesh", "neha", "priya", "deepak"); List result = names.stream() .filter(name -> name.startsWith("d")) .map(String::toUpperCase) .sorted() .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(result); } } Output:
[DEEPAK, DEEPESH, DIKSHA]
Features of Stream API:
-
No Data Storage:
- Streams only process data — they do not store or modify the original data source.
-
Functional & Declarative:
-
Allows writing clean, readable code in a functional style (no explicit
fororwhileloops).
-
Allows writing clean, readable code in a functional style (no explicit
-
Method Chaining:
-
Supports chaining multiple operations like
filter(),map(),sorted()for better readability.
-
Supports chaining multiple operations like
-
Lazy Processing:
-
Intermediate operations are executed only when a terminal operation (like
collect()orforEach()) is called.
-
Intermediate operations are executed only when a terminal operation (like
-
Parallel Processing:
-
Easily process data in parallel using
parallelStream()to take advantage of multi-core processors.
-
Easily process data in parallel using
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



