Immutable Strings in Java
Introduction
-
In Java,
Stringobjects are immutable, meaning once aStringobject is created, its value cannot be changed or modified. -
Any operation that appears to modify a
Stringwill always create a new object instead. -
For example :-
String s1 = "Hello"; s1.concat(" World"); // Creates a new object, does not change s1 System.out.println(s1); // Output: Hello -
Below is a diagram illustrating above example:
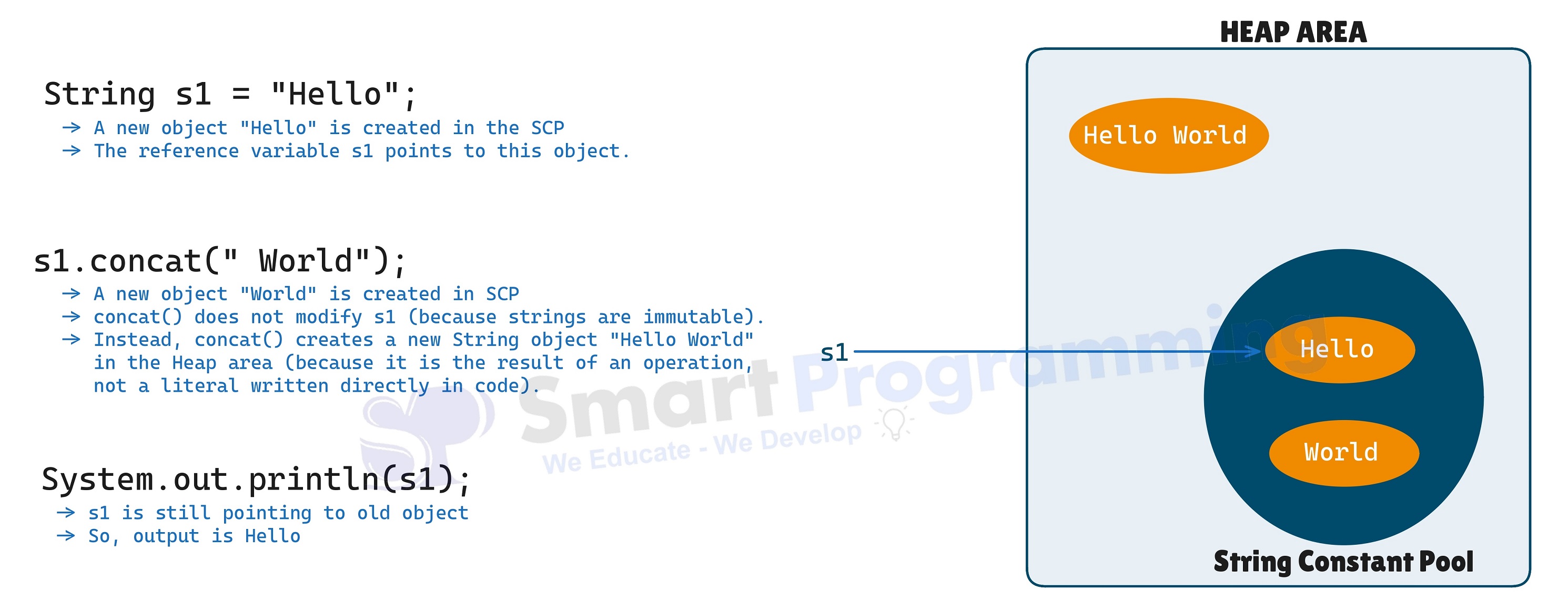
Why String Objects are Immutable?
-
Shared References in String Pool:
- Java stores string literals in a special memory area called the String Constant Pool (SCP).
- Many variables can point to the same string object in the pool.
- If strings were mutable (changeable), updating one reference would also change it for others.
-
To avoid this problem,
Stringobjects are made immutable.
-
Security:
- Strings are used to store important information like passwords, URLs and database connection details.
- If strings could be changed, malicious code could modify this data and cause security issues.
- Immutability ensures that once a string is created, its value is safe and cannot be altered.
-
Caching & Reusability:
-
Because strings are immutable, the same
Stringliteral can be reused by different variables. - This avoids creating duplicate objects and helps in saving memory.
-
Because strings are immutable, the same
-
Thread-Safety:
-
In multi-threaded programs, many threads can use the same
Stringobject at the same time. - Since the value of a string cannot change, it is automatically thread-safe.
-
In multi-threaded programs, many threads can use the same
-
Performance in Hashing:
-
Strings are commonly used as keys in collections like
HashMapandHashSet. -
Because strings are immutable, their
hashCode()value is always constant. -
This makes searching and storing in
HashMaporHashSetmuch faster and reliable.
-
Strings are commonly used as keys in collections like
Help Us Get Better Every Day
Your feedback helps us grow! If there's anything we can fix or improve, please let us know.
We’re here to make our tutorials better based on your thoughts and suggestions.



